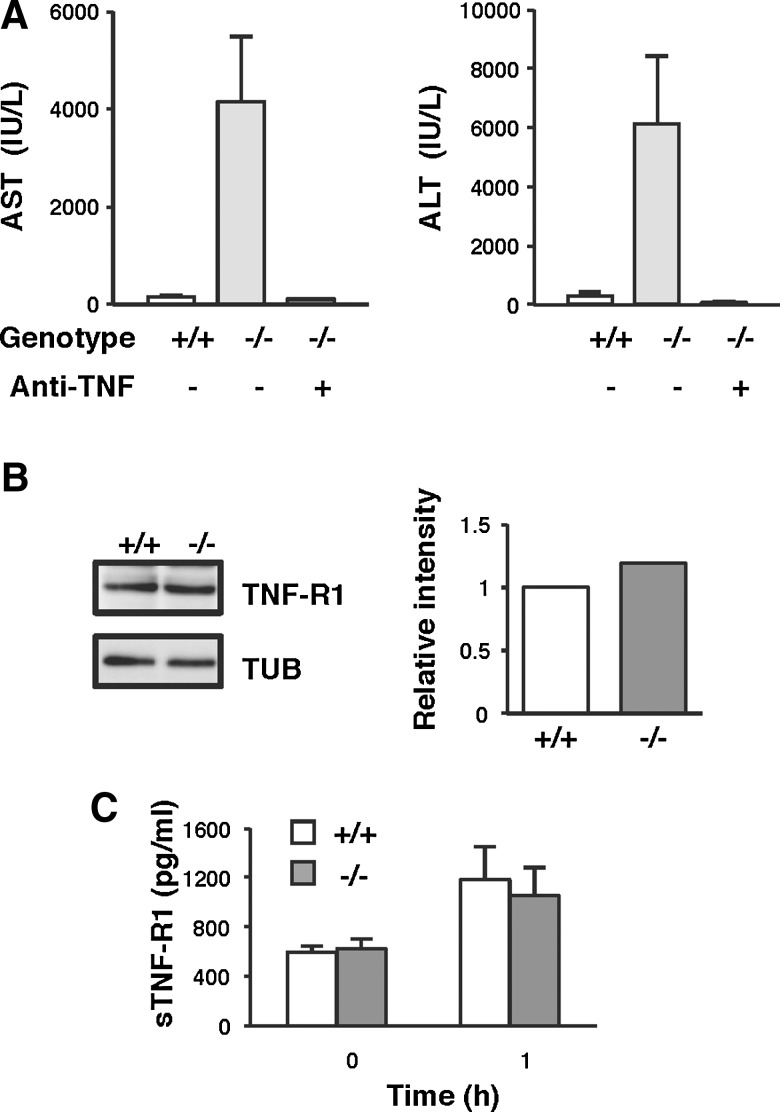
FIG. 6.
TNF-α is a critical effector of hepatotoxicity induced by LPS/GalN in TMX−/− mice. (A) Inhibition of TNF-α protects the liver from LPS/GalN-induced damage. Mice were intraperitoneally injected with saline (−) or anti-TNF-α-neutralizing antibodies (+) 6 h before LPS/GalN administration. Serum levels of AST and ALT were measured 24 h after the LPS/GalN challenge. Data represent the mean values±SD of two to three animals. (B) Immunoblots of liver extracts for TNF-R1 and TUB. The protein expression of TNF-R1 was quantified and normalized to TUB. (C) Serum levels of soluble TNF-R1 (sTNF-R1) were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay before and 1 h after injection of LPS/GalN. sTNF-R1 generated by the proteolytic cleavage of the molecule on the cell surface has been shown to bind TNF-α and regulate circulating TNF-α activity. Concentrations of sTNF-R1 were measured in duplicate, and data represent the mean values±SD of six animals.