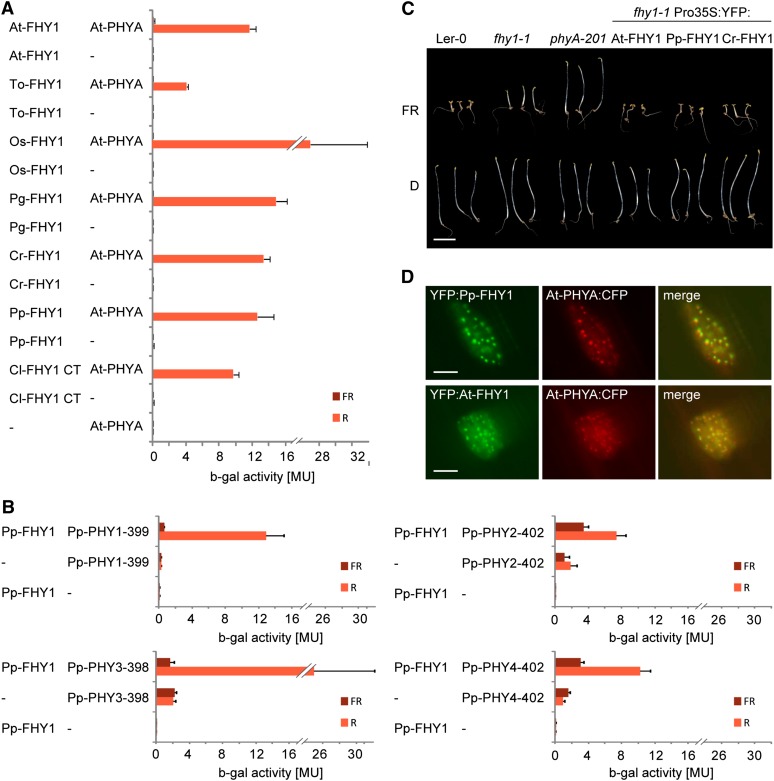
Figure 3.
Cryptogam and Seed Plant FHY1 Are Functional Homologs.
(A) Cryptogam FHY1 proteins contain a PHYA binding motif. AD plasmids containing the coding sequence for the C-terminal phytochrome binding motif of FHY1 from Closterium sp (Cl; green algae) or full-length FHY1 from Arabidopsis (At), dandelion (Taraxacum officinale; To), rice (Oryza sativa; Os), white spruce (Picea glauca; Pg), Ceratopteris richardii (Cr; fern), or P. patens (Pp) fused to the GAL4 activation domain were used for yeast two-hybrid analysis with Arabidopsis PHYA fused to the GAL4 DNA binding domain. To convert PHYA to the Pfr or Pr form, yeast cultures were irradiated for 5 min with R (12 μmol m−2 s−1) or FR light (12 μmol m−2 s−1) and incubated for 4 h in the dark before measuring the β-galactosidase activity. MU, Miller Units; Error bars represent se; n = 3.
(B) P. patens phytochromes interact with Pp-FHY1 in a light regulated fashion. N-terminal fragments of P. patens phytochromes fused to the binding domain were used for yeast two-hybrid assays with AD:Pp-FHY1 as described in (A). MU, Miller Units; Error bars represent se; n = 3.
(C) P. patens and Ceratopteris FHY1 are functional in Arabidopsis. Landsberg erecta-0 (Ler-0), fhy1-1, and phyA-201 as well as fhy1-1 seedlings expressing 35S promoter–driven YFP:At-FHY1, YFP:Pp-FHY1, or YFP:Cr-FHY1 were grown for 5 d in darkness (D) or FR (12 μmol m−2 s−1). Bar = 5 mm.
(D) Pp-FHY1 and At-PHYA colocalize in light-induced nuclear bodies. Etiolated mustard seedlings were transformed by particle bombardment with constructs coding for Pro35S:PHYA:CFP and either Pro35S:YFP:At-FHY1 or Pro35S:YFP:Pp-FHY1. After transformation, the seedlings were incubated for 2 d in darkness and used for microscopy. The images were acquired after 5 min irradiation with W light. Bars = 10 μm.