Figure 5.
HIR-Like Responses to High Fluence Rate FR Light in P. patens.
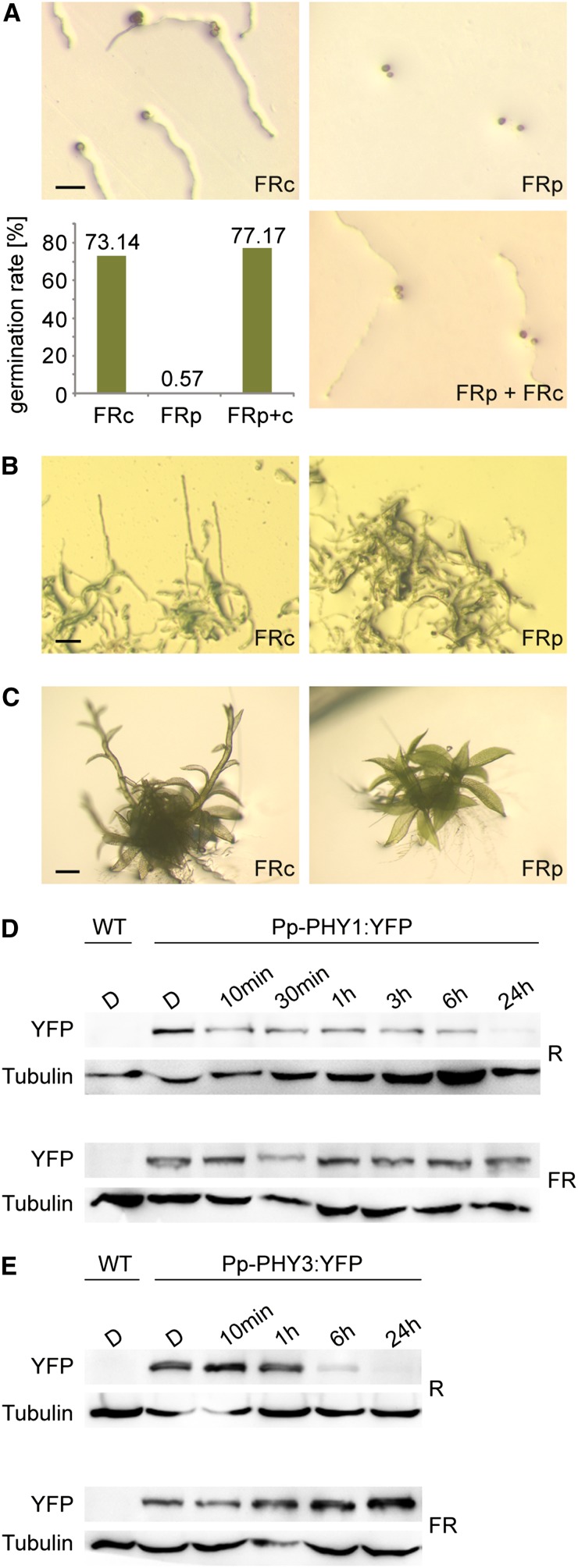
(A) Spore germination in FR light requires continuous irradiation. P. patens spores were irradiated for 3 d with continuous FR light (FRc; 3.5 μmol m−2 s−1) or with 3-min FR light pulses (FRp; 70 μmol m−2 s−1) of the same total fluence, interrupted by 57-min dark periods. To ensure that spores irradiated with FR pulses were viable, they were irradiated for an additional 3 d with continuous FR light (FRp + FRc). The bar plot shows significantly reduced germination rate in FRp (Fisher’s exact test P < 2.2e-16). Bar = 100 μm.
(B) Protonemata growth in FR light depends on continuous irradiation. P. patens cultures were grown for 20 d in continuous FR light (3.5 μmol m−2 s−1) or irradiated with 3-min FR light pulses (70 μmol m−2 s−1) of the same total fluence, interrupted by 57-min dark periods. For dark controls, see Supplemental Figure 8B online. Bar = 100 μm.
(C) Continuous irradiation is essential for FR light–induced gametophore growth. P. patens gametophores were grown for 9 d in continuous FR light (3.5 μmol m−2 s−1) or irradiated with 3-min FR light pulses (70 μmol m−2 s−1) of the same total fluence, interrupted by 57-min dark periods. For dark controls, see Supplemental Figure 8C online. Bar = 500 μm.
(D) Pfr-dependent degradation of Pp-PHY1. Dark-adapted protonemata cultures of P. patens lines expressing YFP-tagged Pp-PHY1 were irradiated with R light (22 μmol m−2 s−1) or FR light (18 μmol m−2 s−1) for different time periods. Total protein was isolated and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-YFP antibody. Protein extracts from dark-adapted wild-type P. patens cultures were used as negative controls. Tubulin is shown as a loading control. D, darkness; WT, the wild type.
(E) Pfr-dependent degradation of Pp-PHY3. Dark-adapted protonemata cultures of P. patens lines expressing Pp-PHY3:YFP were irradiated with either R or FR light and used for SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis as described in (D).
[See online article for color version of this figure.]