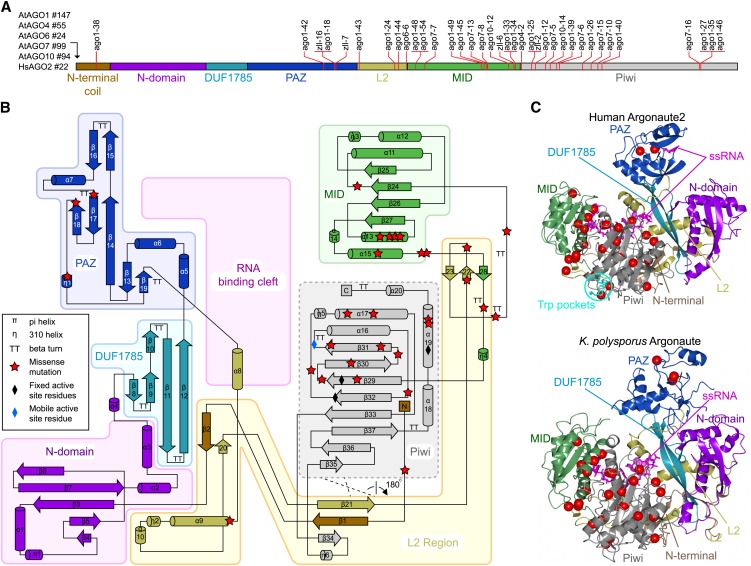
Figure 1.
Structural Mapping of AGO Missense Mutations.
(A) Schematic diagram of common elements of the primary structure of the AGO protein family depicting the location of known plant missense alleles. The length of N-terminal extensions in each AGO protein is shown to the left of the diagram.
(B) Topology diagram of the human Ago2 structure colored according to domains and structural regions. The RNA binding cleft is located between one lobe containing the N, DUF1785, and PAZ domains and a second lobe containing the MID and Piwi domains. The L2 connects the two lobes and forms secondary structure elements with several domains and the structured N terminus. The plant ago missense mutations are marked with red stars.
(C) The tertiary structures of human Ago2 and K. polysporus Ago as determined by crystallography. Note the overall structural similarity between human and yeast Ago, except in the PAZ domain that exists in closed (human Ago2) and open (K. polysporus Ago) conformations. The positions of plant ago missense mutations are marked with red spheres. ssRNA, single-stranded RNA.