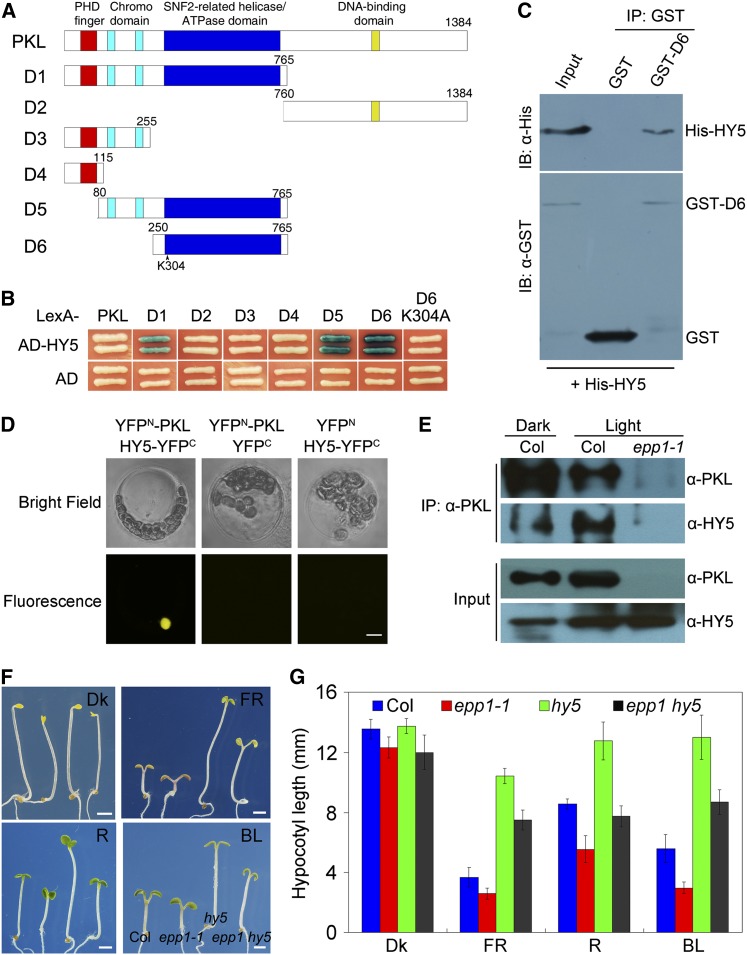
Figure 4.
PKL and HY5 Interact with Each Other.
(A) Diagram of the domain structures of PKL and various PKL deletions (D1-6).
(B) Yeast two-hybrid assay between various fragments or mutant forms of PKL shown in (A) fused to the LexA DNA binding domain and AD-tagged HY5 (AD-HY5) or AD alone.
(C) Pull-down assay showing direct interaction between GST-PKL-D5 and His-HY5 fusion proteins in vitro. IB, immunoblotting; IP, immunoprecipitation.
(D) BiFC assay showing that YFPN-PKL and HY5-YFPC interact to form a functional YFP in the nucleus. Bar = 5 μm.
(E) Coimmunoprecipitation assay showing that the PKL antibody could precipitate HY5 in 5-d-old Col wild-type seedlings grown in both white light (1.5 μmol m−2 s−1) and darkness.
(F) Seedling phenotypes of hy5, epp1-1, and epp1 hy5 mutants and the Col wild type after exposure to red (R), far-red (FR), blue light (BL), or darkness (Dk) for 5 d. The seedlings are arranged in identical order in each panel. Bars = 2 mm.
(G) Quantification of hypocotyl length of the wild-type and mutant seedlings shown in (F). Data represent the mean ± sd of 30 seedlings.