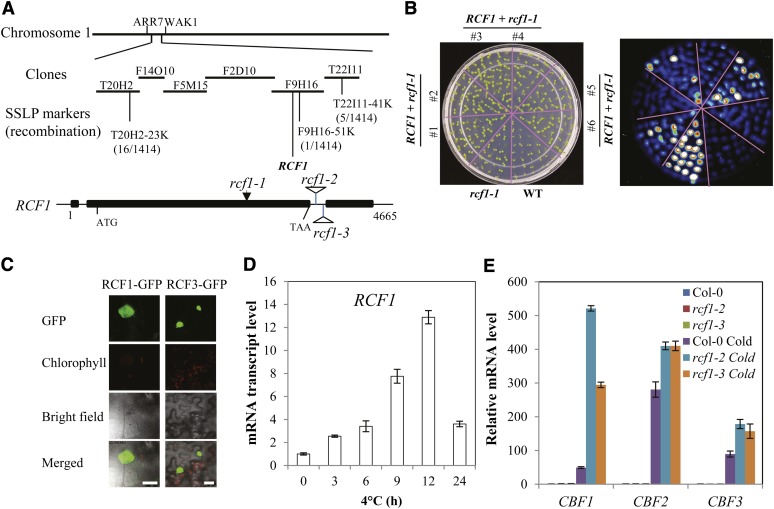
Figure 3.
Molecular Cloning of RCF1.
(A) Positional cloning of RCF1. Numbers of recombination are from 1414 F2 progeny seedlings that are homozygous for rcf1-1 phenotypes. The rcf1-1 mutation is caused by a single-nucleotide substitution (from G to A at position 2650, relative to transcription start site), and this mutation changes amino acid Gly-808 to Arg. Structure of the RCF1 gene and positions of rcf1-1, rcf1-2, and rcf1-3 mutations are indicated. Filled boxes indicate exons, and lines between boxes indicate introns.
(B) Molecular complementation of the rcf1-1 mutant by the wild-type (WT) RCF1 gene. Shown are seedlings on an MS agar plate (left) and the corresponding luminescence image after 4°C treatment for 24 h (right).
(C) RCF1-GFP is localized in the nucleus of tobacco leaf epidermal cells. RCF3-GFP fusion protein was used as a positive control (Guan et al., 2012). Bars = 25 µm.
(D) Time-course expression of RCF1 in 14-d-old wild-type seedlings.
(E) Transcript levels of CBF1, CBF2, and CBF3 in Col-0, rcf1-2, and rcf1-3 seedlings subjected to 0 or 12 h at 4°C. Error bars in (D) and (E) indicate the sd (n = 4).