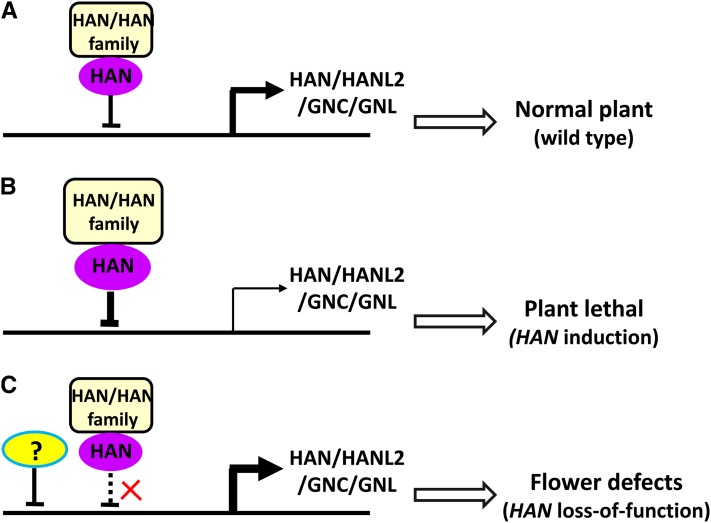
Figure 11.
A Model for HAN Function in Arabidopsis.
(A) In the wild-type plant, HAN interacts with itself and with its family genes in a negative feedback loop, which decreases the transcription of HAN, HANL2, GNC, and GNL to produce the moderate level of expression necessary for normal plant development.
(B) Transient overexpression of HAN enhances transcriptional repression, which results in substantially reduced expression of endogenous HAN and GATA3 family genes and therefore has deleterious effects on plant development.
(C) In the han mutant background, reduced HAN protein levels result in weakened transcriptional repression and higher HANL2, GNC, and GNL expression. The levels are not much higher than in wild-type plants, which may indicate that an alternative (and unknown) repressor is triggered to down-modulate the expression of GATA3 family genes, producing a plant with floral developmental defects, but not complete deregulation of the GATA3 family genes.