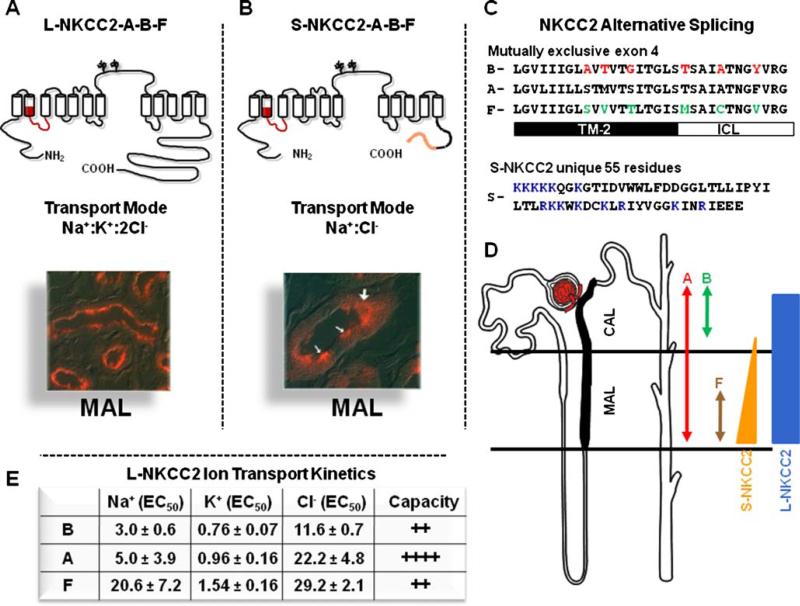
Fig. 2.
Molecular physiology of the Na+:K+:2Cl– co-transporter, NKCC2. a Topology, transport mode, and immunolocalization of the long isoform of NKCC2 (L-NKCC2). There are 12 transmembrane spanning segments and a long hydrophilic loop between TM 7 and 8, with two glycosylation sites. Location of the mutually exclusive cassette exons is shown in red. b Topology, transport mode, and immunolocalization of the short isoform of NKCC2 (L-NKCC2). Location of the mutually exclusive cassette exons is shown in red and the unique 55 piece at the end is shown in orange. White arrows in the picture show positive cells. c Sequence and alignment of the alternative splicing of SLC12A1. The 31 residues of the three exons are shown. Switching the red or green residues between B and F isoforms is enough to switch their ion transport kinetics between each other. TM-2 transmembrane domain 2. ICL Interconnecting segment between TM2 and TM3. The 55 unique piece of S-NKCC2 is shown. Residues in blue are positively charged. d Distribution of L-NKCC2 and S-NKCC2, as well as exons A, B, and F along TAL, as stated. e Ion transport kinetics and capacity of transport for L-NKCC2 A, B, and F variants, as informed by Plata et al. [113]