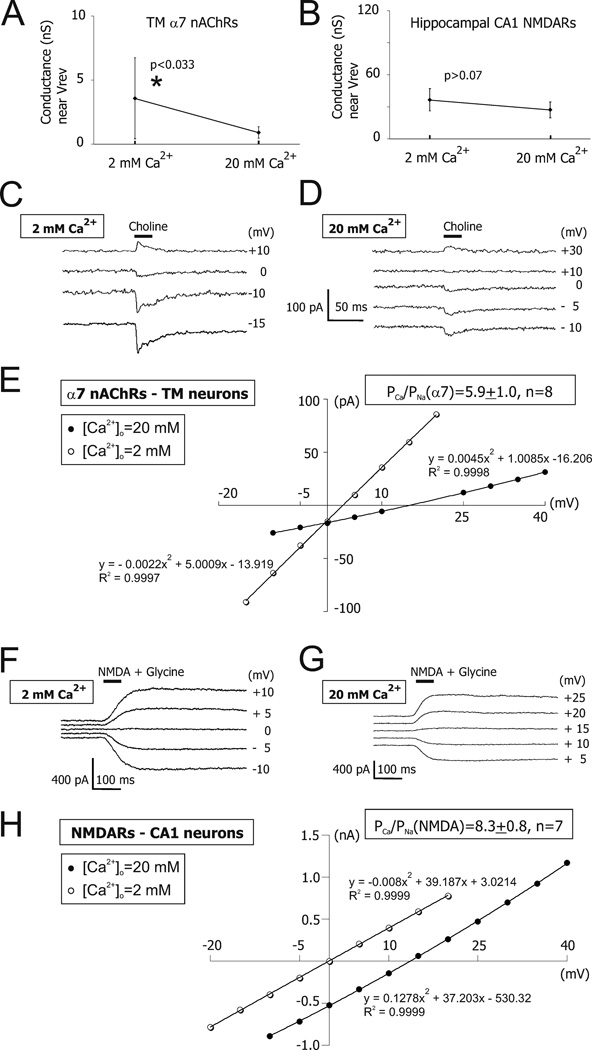
Figure 1. The whole-cell conductances of α7 nAChR- and NMDAR-mediated responses near the reversal potential.
The mean and standard deviation of the slope conductance near Vrev built for TM α7 nAChR- (A) and hippocampal CA1 pyramidal NMDAR-mediated responses (B). A significant [Ca2+]o–dependent decrease in the whole-cell conductance of TM α7 nAChR-, but not CA1 NMDAR-mediated responses was observed (97). This decrease was not due to a current rundown because it persisted in experiments where high (i.e., 20 mM) [Ca2+]o was used before low (i.e., 2 mM) [Ca2+]o (97). Examples of TM α7 nAChR-mediated currents obtained by applications of choline at various positive and negative membrane voltages in voltage-clamp in 2 mM [Ca2+]o (C) and 20 mM [Ca2+]o (D). The whole-cell conductance of TM α7 nAChR channels in high [Ca2+]o was always lower than that in low [Ca2+]o, presumably due to a Ca2+-dependent block of monovalent ion permeation. E) The current-voltage relationship for responses illustrated in (C) and (D). No considerable current rectification was observed owing to Mg2+-free external and internal solutions and the presence of F− ions in the internal solution. The I–V curves were fitted with second-order polynomial equations. Panels C–E illustrate data obtained from the same acutely dissociated TM neuron. Examples of CA1 NMDAR-mediated currents obtained by applications of NMDA plus glycine at various positive and negative membrane voltages in voltage-clamp in 2 mM [Ca2+]o (F) and 20 mM [Ca2+]o (G). H) The current-voltage relationship for responses illustrated in (F) and (G). The whole-cell conductance of NMDAR channels in 20 mM [Ca2+]o was similar to that in 2 mM [Ca2+]o, indicating a lack of significant Ca2+-dependent block of monovalent ion permeation. The I–V curves were fitted with second-order polynomial equations. Panels F–H illustrate data obtained from the same acutely dissociated hippocampal CA1 neuron. Note that although the application pipettes were filled with 40 mM choline or 200 µM NMDA + 20 µM glycine, the effective concentrations of choline or NMDA+glycine near the recorded neurons were unknown and considerably lower than the concentrations of agonists in application pipettes. However, in each given experiment these concentrations were very stable evidenced by stable responses (97). Reprinted from (97) with permission from Blackwell Publishing in the format Journal via Copyright Clearance Center.