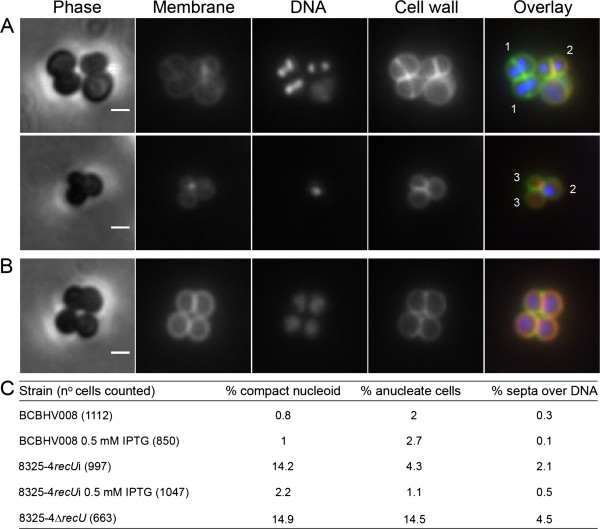
Figure 2.
RecU depletion in S. aureus leads to chromosome segregation defects. The fluorescence microscopy images show cells of recU inducible strain 8325-4recUi incubated in the absence (A) or presence (B) of IPTG. Panels from left to right show phase-contrast images, cells stained with membrane dye Nile Red, DNA dye Hoechst 33342, cell wall dye Van-FL and the overlay of the three fluorescence images showing the membrane in red, the DNA in blue and the cell wall in green. The absence of RecU (A) led to the formation of cells with septa bisecting the DNA (1), compact nucleoids (2) and anucleate cells (3). Ectopic expression of RecU in 8325-4recUi strain, through the addition of IPTG, resulted in the disappearance of the aberrant phenotypes (B). Scale bars 1 μm. Panel (C) shows a comparison of the phenotypes of control strain BCBHV008; 8325-4recU inducible mutant, incubated in the presence or absence of IPTG and 8325-4ΔrecU mutant.