Fig 4.
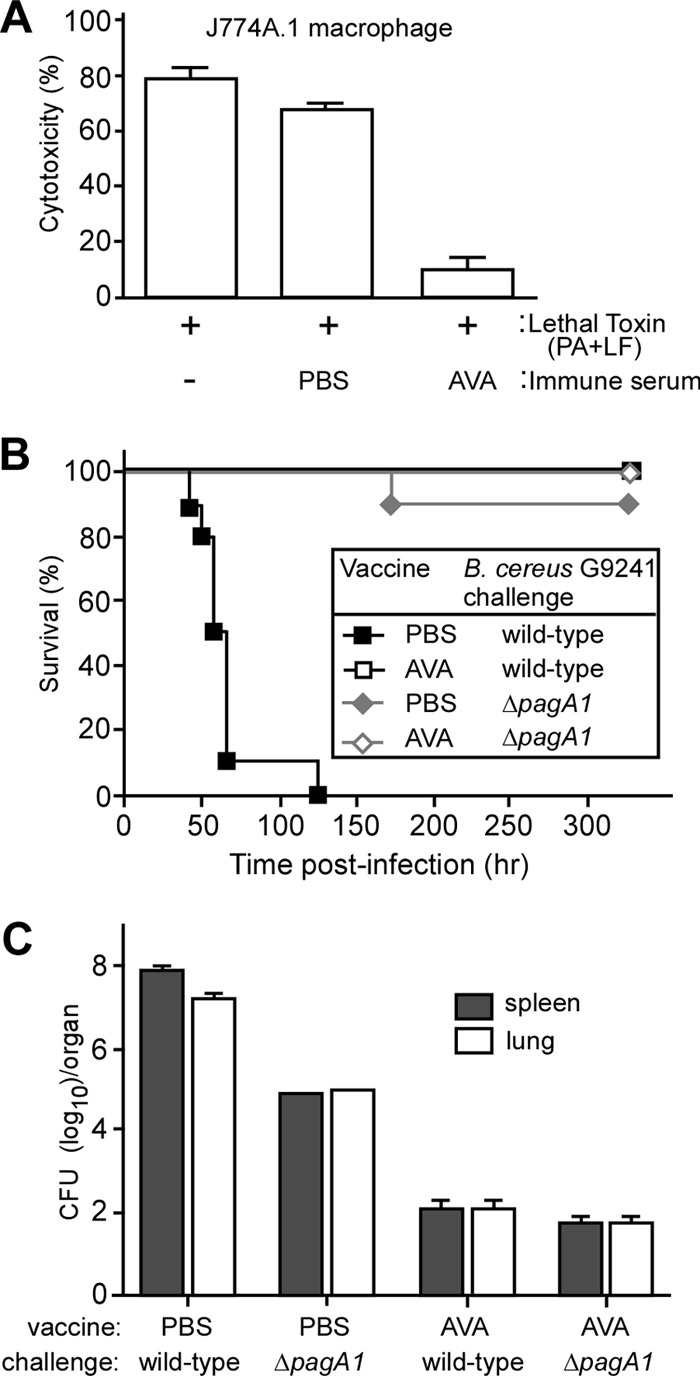
AVA-immunized mice are protected against B. cereus G9241 challenge. (A) Lethal toxin neutralization assay. Serum from mock (PBS)-immunized or AVA-immunized C57BL/6 mice was incubated with 0.1 μg anthrax lethal toxin (PA + LF), and the toxin-serum mix as well as a no-serum control reaction mixture was transferred to 105 J774A.1 cells. Cell viability was monitored with an LDH-based cytotoxicity assay after 3 h of incubation. (B) C57BL/6 mice (n = 10) were immunized with a prime-booster regimen of AVA or mock (PBS) in 14-day intervals. Animals were challenged by intraperitoneal inoculation with 1 × 105 spores derived from the B. cereus G9241 wild type or its ΔpagA1 mutant, and survival was monitored. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Bacterial loads in spleen and lung tissues of immunized mice that had been infected with either B. cereus G9241 wild type or its ΔpagA1 mutant. The organs of mock-immunized mice were removed during necropsy when animals were either dead or moribund. Tissue homogenates were spread on agar plates to enumerate colony formation. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
