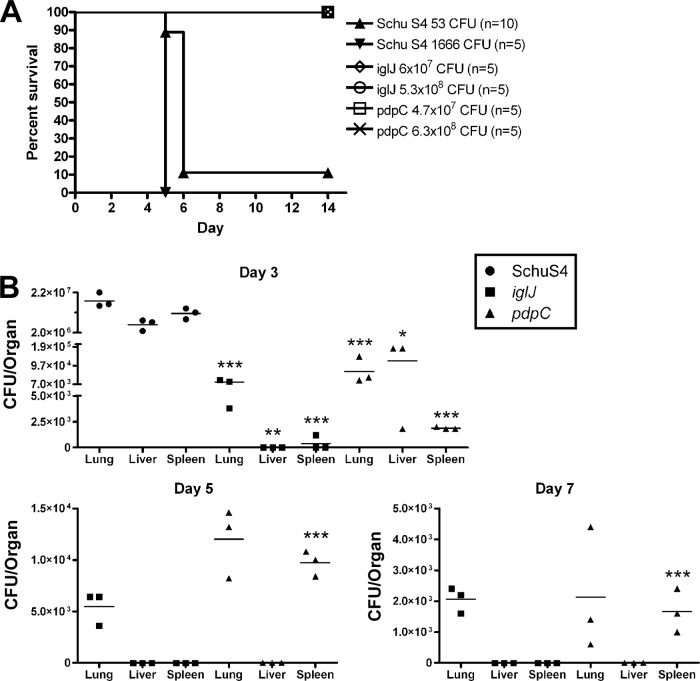
Fig 9.
In vivo virulence and dissemination assays confirm the distinct phenotype of the pdpC mutant. (A) Groups of 5 or 10 BALB/c mice were infected intranasally with the indicated dose of wild-type or mutant bacteria. The data shown are from a representative experiment and demonstrate that both the iglJ and pdpC strains are highly attenuated at ∼108 CFU while wild-type Schu S4 is lethal at 53 CFU, and mice succumb to infection by day 5 or 6. (B) Mice in groups of three were intranasally infected with 5.67 × 106 CFU iglJ, 3.0 × 106 CFU pdpÇ or 2.0 × 103 CFU Schu S4 strain. Dissemination from the lungs to the liver and spleen was determined by plating organ homogenates for enumeration of CFU on days 3, 5, 7, and 14 postinfection. Schu S4 data are shown only for day 3, as all mice succumbed by day 5. By day 14, iglJ and pdpC bacteria had been cleared and were not detected (data not shown). Horizontal lines indicate the mean results for each group of mice at each time point. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 versus Schu S4 (day 3) or iglJ (day 5 and 7) samples.