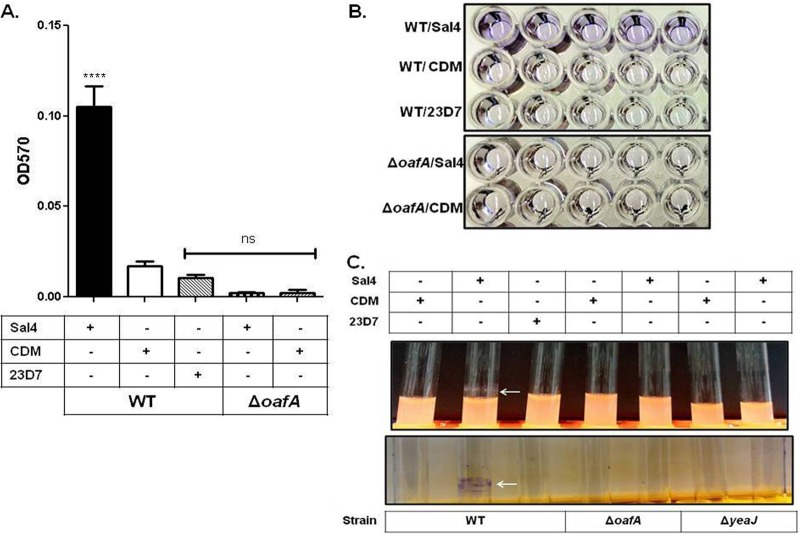
Fig 1.
S. Typhimurium biofilm formation in response to Sal4. WT and JA001 (ΔoafA) strains of S. Typhimurium in LB broth were incubated on microtiter plates or in borosilicate glass culture tubes at 37°C for 24 h in the presence of Sal4 (15 μg/ml), 23D7 (15 μg/ml), or chemically defined medium (CDM). The cultures were then assayed for EPS production using CV, as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Quantification of biofilm mass, as measured by absorbance (optical density) at 570 nm (OD570). Statistical significance was determined by a one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni's correction, compared to the WT strain treated with CDM. ****, P < 0.0001; ns, nonsignificant. Each bar represents the mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM). (B) Representative images of CV-stained microtiter plates highlighting the effect of Sal4 on WT S. Typhimurium (top panel, top row). In contrast, there was no EPS production by strain JA001 (ΔoafA) in response to Sal4 (bottom panel), demonstrating the specificity of the antibody response. (C) Representative images demonstrating pellicle formation (top panel) and EPS production (bottom panel) on borosilicate culture tubes in response to Sal4 (arrows). The data in each panel represent the averages of three independent assays. In each assay, experimental samples were performed in five-replicate (quintuplicate) wells or culture tubes.