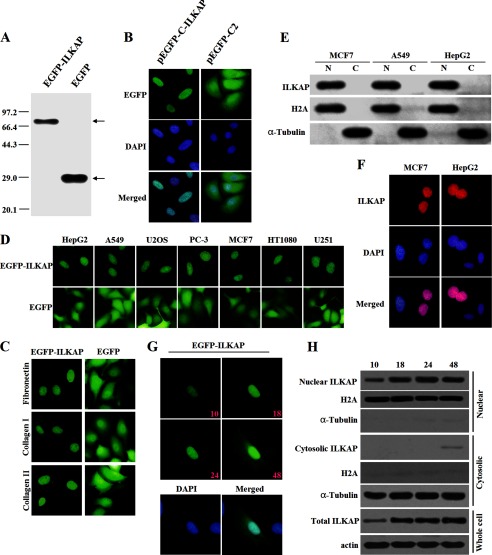
FIGURE 2.
Subcellular distribution of tagged ILKAP. A, detection of the protein expression of the full-length EGFP-ILKAP and the EGFP empty constructs. MCF7 cells were transiently transfected with each construct and allowed to recover for 24 h. The protein expression was confirmed by immunoblotting using an anti-EGFP antibody. B, localization of EGFP-ILKAP and EGFP in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells were transiently transfected with the respective constructs and grown on coverslips for 24 h after transfection. The cells were then fixed and counterstained with DAPI for nuclear staining (blue). C, localization of EGFP-ILKAP and EGFP in MCF7 cells grown on coverslips coated with fibronectin (10 mg/ml), collagen type I (5 mg/ml), or collagen type IV (5 mg/ml). D, localization of EGFP-ILKAP and EGFP in different cell lines. E, the subcellular localization of EGFP-ILKAP was examined by cell fractionation and immunoblotting. HepG2, A549, and MCF7 cells were separated into nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) fractions, and the protein expression levels were analyzed with anti-EGFP, anti-H2A, and anti-α-tubulin antibodies. F, distribution of the Myc-ILKAP fusion protein in MCF7 and HepG2 cells. MCF7 and HepG2 cells were immunostained with anti-Myc antibody. The protein localization was detected using a Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody. G, time-lapse images of EGFP-ILKAP in A549 cells after transfection. The protein was detected through the microscopic observation of EGFP (green) over a period of 48 h. The merged image was formed by merging the images that were obtained 48 h after transfection. H, immunoblotting analysis of EGFP-ILKAP by cell fractionation.