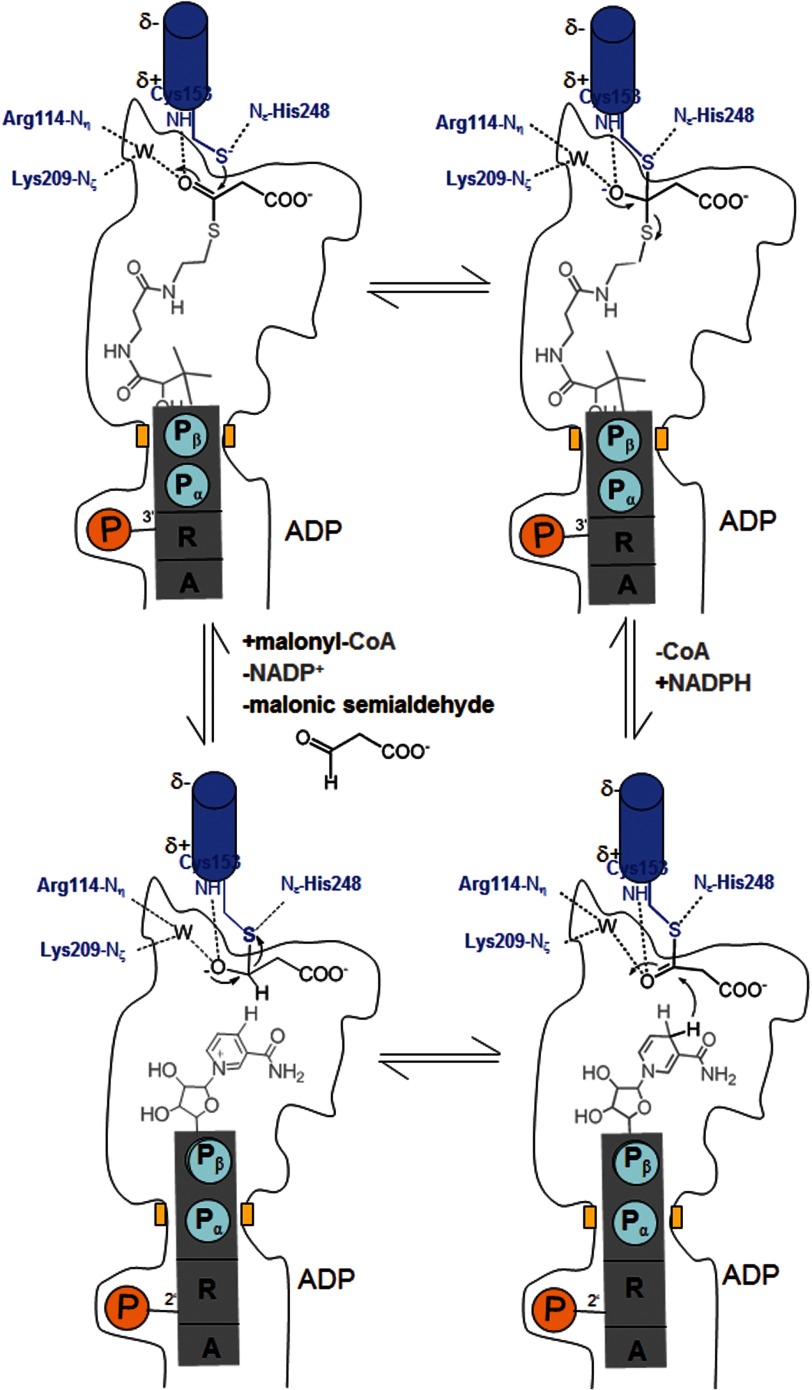
FIGURE 5.
Proposed enzymatic mechanism. A, malonyl-CoA is bound and subsequently attacked by the Cys153 thiolate forming a tetrahedral intermediate. The negative charge of the oxyanion is stabilized by basic residues and by the positively charged N-terminal end of helix 152:168. B, the tetrahedral intermediate is converted to a thioacyl adduct, CoA is released, and NADPH is bound. CoA and NADPH use an identical binding site. C, NADPH transfers a hydride from the B-side to the thioacyl carbon forming a hemithioacetal intermediate, which is converted to the product malonic semialdehyde, thereby restoring Cys153 (D).