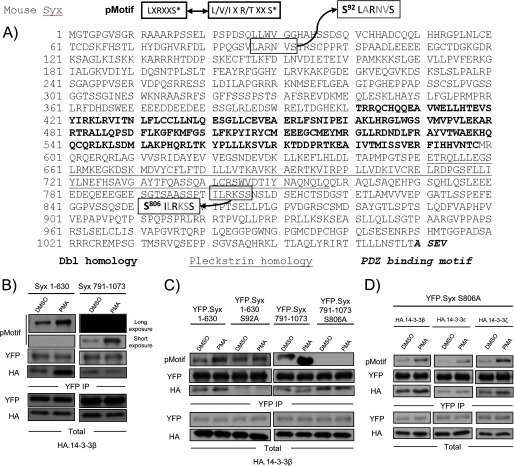
FIGURE 3.
PMA/PKD mediated phosphorylation of Syx at Ser92. A, Ser92 is a putative PKD phosphorylation site. The pMotif antibody recognizes a consensus motif that contains a leucine at the −5 position and an arginine at the −3 position. Ser92 and Ser806 are the only residues within Syx that conform to the consensus motif. B, Syx(1–630) is a PKD phosphorylation target. HeLa cells were co-transfected with the indicated constructs and subjected to DMSO (control) or PMA (100 nm, 10 min) treatment prior to immunoprecipitation. Protein samples were analyzed by Western blot. X-ray film was exposed to the same blot for different lengths of time to visualize the phosphorylation (by pMotif) of Syx(1–630) and Syx(791–1073). C, both control and PMA-induced 14-3-3 associations require Syx Ser92. As in B, transfected cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation after treatment with DMSO (control) or PMA (100 nm, 10 min). Protein samples were analyzed by Western blotting. Note that the mutation of Ser92 to alanine abrogated the PMA-induced increase in phosphorylation seen with pMotif in Syx(1–630). D, Ser92 is phosphorylated by PKD in addition to Ser806. A PMA-induced increase in pMotif phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding was observed upon transfecting cells with full-length Syx mutant YFP-Syx S806A. As in B, transfected cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation, and protein samples were analyzed by Western blotting.