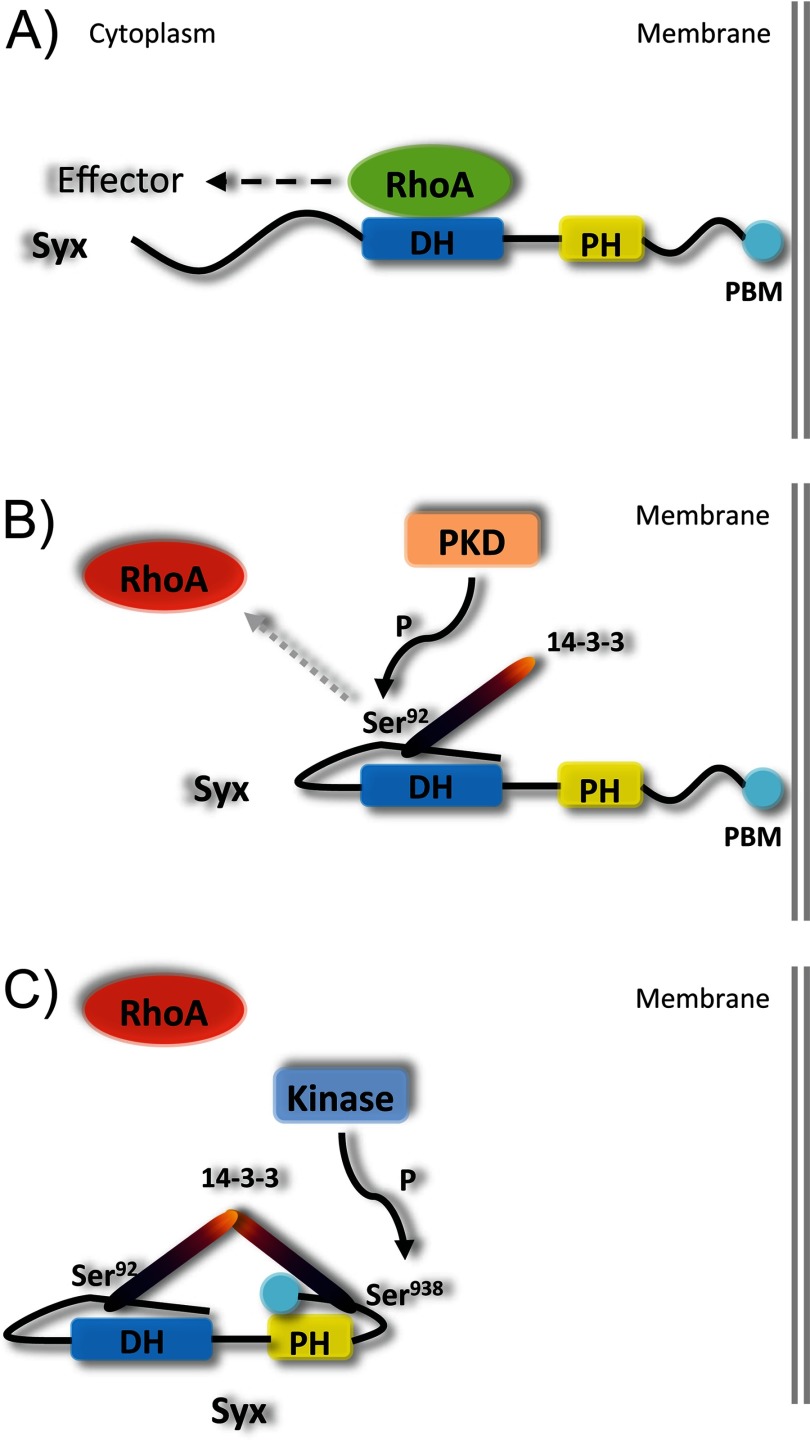
FIGURE 7.
Proposed mechanism of PKD-mediated 14-3-3 binding to Syx. A, membrane-localized Syx activates RhoA locally. B, PKD-mediated phosphorylation of Ser92 upon proper folding of Syx N terminus induces binding of 14-3-3 protein. C, phosphorylation of Ser938 promotes 14-3-3 binding at the C terminus. Additional phosphorylation of Ser806 (data not shown) by PKD induces conformational changes to the C terminus and brings the two 14-3-3 proteins into close proximity. As a consequence, dimerization of terminally bound 14-3-3 proteins locks Syx in an inactive state (suppresses GEF activity), and Syx is displaced from areas of cell-cell contact. PH, pleckstrin homology domain; DH, Dbl homology domain.