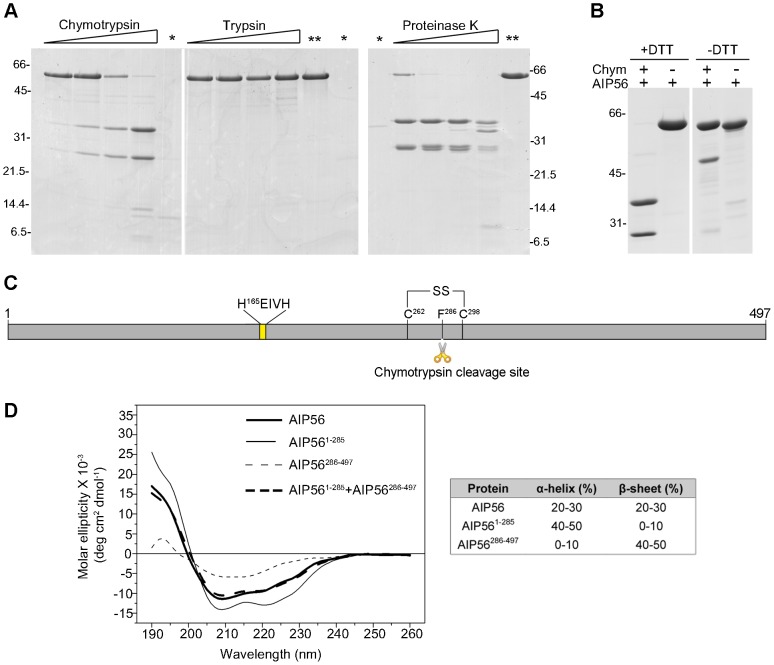
Figure 2. AIP56 is composed of two domains linked by a disulphide bridge.
(A) Limited proteolysis of AIP56 with chymotrypsin and proteinase K produces two major fragments. AIP56 (0.6 mg/ml) was incubated with 0.25, 1.25, 6.25 or 25 µg/ml of chymotrypsin, trypsin and proteinase K for 30 min on ice and digests analysed by reducing SDS-PAGE. The proteases (marked as *) and undigested AIP56 (marked as **) were loaded as controls. (B) The two AIP56 digestion fragments are linked by a disulphide bridge. AIP56 was incubated with or without 25 µg/ml chymotrypsin (Chym) for 30 min on ice and digests analysed under reducing (+DTT) or non-reducing (−DTT) SDS-PAGE. Numbers to the left and right of the panels refer to the position and mass of the molecular weight markers, in kDa. (C) Schematic representation of AIP56. (D) Far-UV CD spectra of AIP56 (thick solid line), AIP561–285 (thin solid line), AIP56286–497 (thin dashed line) and the weighted sum of AIP561–285 and AIP56286–497 spectra (thick dashed line).