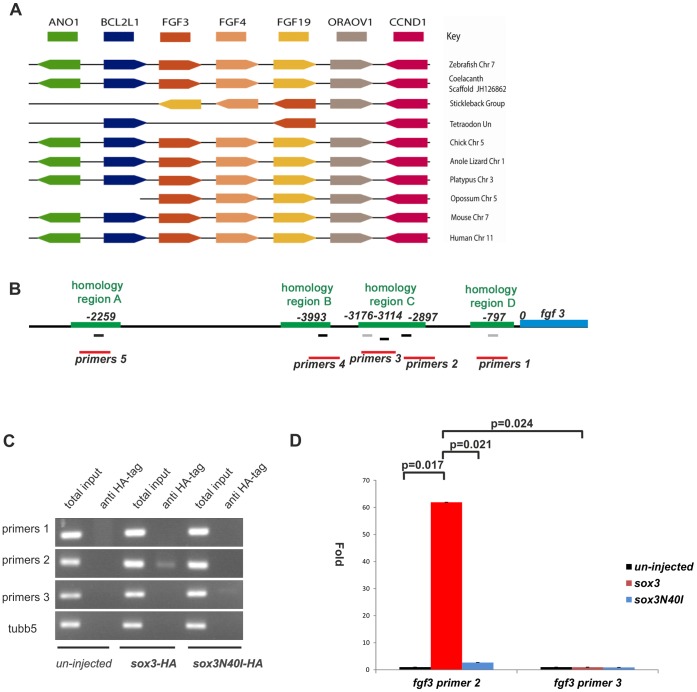
Figure 2. Sox3 can directly bind to a region upstream of fgf3.
(A) Synteny in the region of the genome flanking the fgf3 gene. Coloured boxes indicate different genes and direction of transcription. Not to scale. Absence of line indicates incomplete genomic scaffold information. (B) Diagram showing the upstream region of fgf3. Green bars indicate regions of homology among different species. The position of potential Sox binding sites (A/T)(A/T)CAA(A/T)G within these homologous regions are shown as black bars and similar potential Sox binding sites lacking the final 3′ “G” are shown as gray bars. The red bars show the PCR products, including the Sox binding sites that would be produced by different primer pairs. (C) 25 pg sox3-HA and sox3N40I-HA RNA were injected at the 1–2 cell stage embryos and harvested at 4.5 hpf. ChIP analysis using an anti-HA antibody to precipitate Sox3 and bound DNA. PCR results after ChIP procedure showed that the DNA fragments pulled down by Sox3-HA can be amplified only by primer pair 2. tubb5 was included as a negative control. (D) Quantitative PCR results of precipitated chromatin using primer pairs 2 and 3 showed that the target sequence for primer pair 2 was significantly enriched following IP of WT Sox3 whereas the target for primer pair 3 was not. Values represented as fold change compared to the uninjected value.