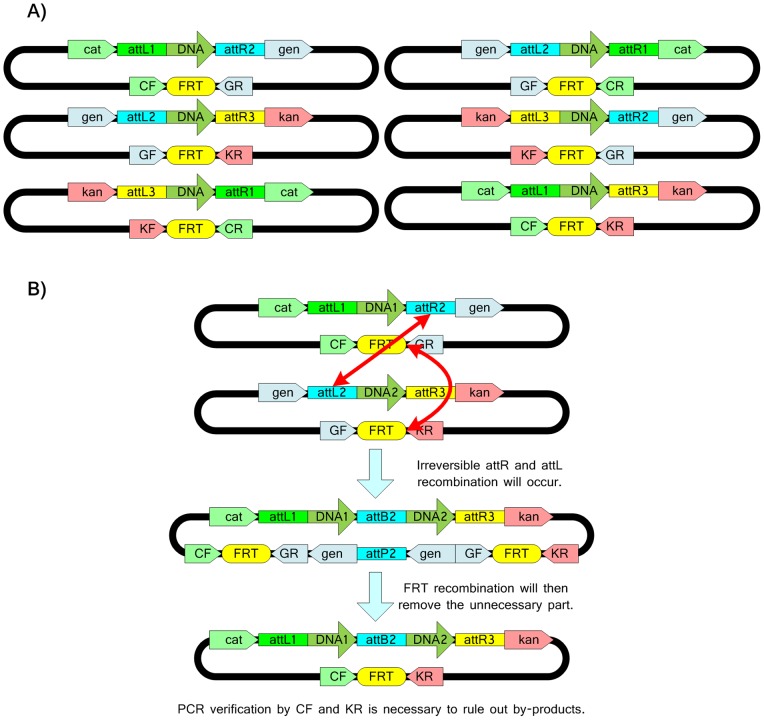
Figure 7. Bi-Swap TRAS.
The design of Bi-Swap TRAS containing the vectors C-DNA-G, G-DNA-K, K-DNA-C, G-DNA-C, K-DNA-G and C-DNA-K (A), where CF, CR, GR, GF, KR and KF are verification primer sites. The chloramphenicol, gentamycin and kanamycin resistance genes are designated cat, gen and kan, respectively. In order to screen a recombination product with a new combination of antibiotic resistance, at least three antibiotic resistance markers must be used. Since the DNA sequence is directional and two antibiotic resistance markers must be different to perform screening, the total number of Unit plasmids is 6 (3×2). In this case, an assembly Unit vector has one Unit vector that can swap and extend its left arm or one Unit vector that can swap and extend its right arm. For example, if C-DNA1-G is the beginning unit, K-DNA2-C can be used to extend the left arm of C-DNA1-G and G-DNA2-K can be used to extend the right arm of C-DNA1-G. The assembly process of the fragments DNA1 and DNA2 (B). G-DNA2-K is used to swap and extend the right arm of C-DNA1-G. Because this is a circular plasmid system, fusion intermediates could form after recombination (but will contain all three antibiotic resistant markers). Therefore, PCR and counter-selection are considered necessary to indentify the correct products.