Figure 5. Embryonic heart IGF2R protein levels following maternal transmission of Igf2r+m/HUp .
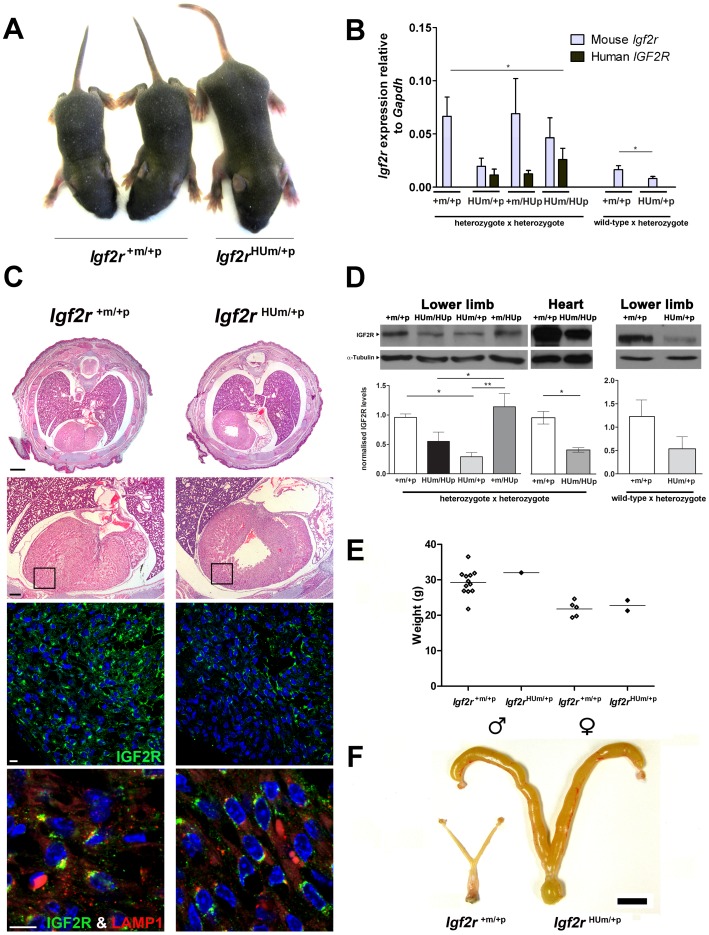
(A) Two wild-type and a surviving Igf2rHUm/+p littermate at post-natal day 7. (B) Q-RT-PCR of Igf2r mRNA expression using mouse and human allele specific primers. Results are shown for progeny of heterozygote inter-cross to generate homozygote humanised knock-in alleles, compared to heterozygote progeny derived from maternal transmission. (*P<0.05, t-test, **P<0.01, 1 way ANOVA, Dunn’s post-test). Note, origin of the humanised allele in the heterozygote progeny was detected by exon 2–3 human and mouse specific RT-PCR. (C) Upper panel; H and E stained example of whole mouse embryo (E18.5) cross-sections below the level of the tracheal bifurcation showing dilated and enlarged heart in Hum. (Bar 1mm). Lower panels; higher power H and E images (Bar 0.25mm) showing regions visualised by immuno-fluoresence labelling of IGF2R (green), LAMP1 (red, for endosomal compartment localisation) and DAPI (nuclear DNA). Relative IGF2R levels appear reduced including the pericardial regions. (Bar 0.1mm). (D)Western blots of IGF2R in mouse embryos at day E18.5 in the lower limb and heart (n = 2–4). IGF2R levels were normalised to α-tubulin. Levels of IGF2R were reduced in limbs and hearts of embryos with a humanised maternal allele (HUm) derived from a heterozygous inter-cross (one way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test, **P<0.005, *P<0.05), Levels of protein following maternal allele transmission alone also appear reduced but were not significant (n = 2). (E) Adult body weights (measured at 10 weeks) of surviving offspring resulting from maternal transmission of the humanised allele (Igf2r+m/HUp females crossed to wild-type males). Wild-type males n = 12 Igf2rHUm/+p males n = 1 wild-type females n = 5 Igf2rHUm/+p females n = 2. (C) Adult uteri from wild-type littermate and Igf2rHum/+p surviving female showing dilated, enlarged and fluid filled uterine horns (scale bar = 1cm).