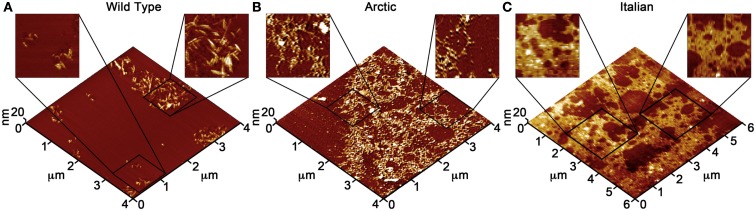
Figure 5.
Point mutations in Aβ influence peptide aggregation in the presence of total brain lipid bilayers. Using solution AFM, aggregation of Wild Type, Arctic (E22G), or Italian (E22K) Aβ in the presence of supported TBLE bilayers was monitored (Aβ concentration was 20 μM for all experiments). 3D images are presented (4 μm × 4 μm and 6 μm × 6 μm) with indicated zoomed in areas of 1 μm × 1 μm and 2 μm × 2 μm shown in 2D. (A) With time, Wild Type Aβ aggregated into discrete oligomers and fibrils that were associated with regions of the bilayer with perturbed morphology (an increase in surface roughness). (B) While many small oligomers of Arctic Aβ were observed on the bilayer, highly curved fibrils that were associated with membrane disruption were the dominant aggregate species. These Arctic Aβ fibrils were morphologically distinct from fibrils observed for Wild Type Aβ. (C) While Italian Aβ also formed similar oligomers compared Wild Type and Arctic Aβ, large patches of disrupted bilayer morphology developed that may be associated with distinct fibril aggregates.