Figure 3.
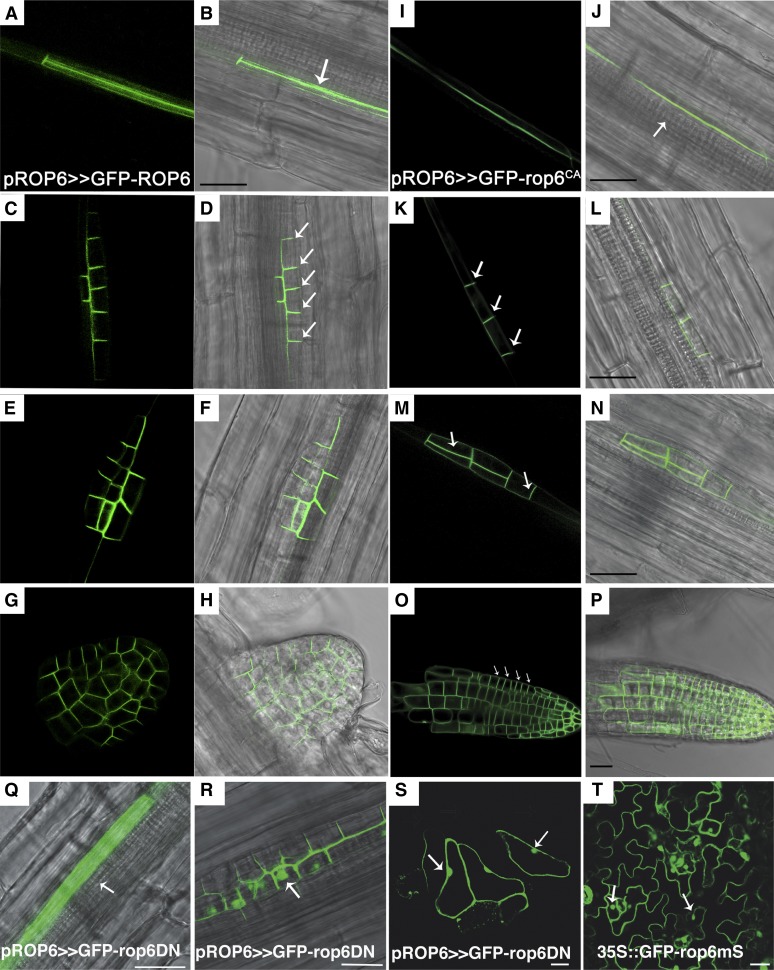
Subcellular localization of GFP-ROP6, GFP-rop6CA, and GFP-rop6DN during lateral root development. Subcellular localizations of GFP-ROP6 (A–H) and GFP-rop6CA (I–P) were observed in developing lateral roots in pROP6>>GFP-ROP6 and pROP6>>GFP-rop6CA seedlings. A, B, I, and J, Lateral root founder cells. GFP-ROP6 and GFP-rop6CA were localized along the side of the cell adjacent to the xylem pole (J, arrow). C, D, K, and L, Stage I/II LRI. The majorities of the GFP-ROP6 and GFP-rop6CA proteins moved and were localized along anticlinal cell borders (arrows). E, F, M, and N, Stage II/III LRI. The majority of GFP-ROP6 and GFP-rop6CA were localized along anticlinal and periclinal cell borders (arrows) separating the newly formed outer and inner layers. G, H, O, and P, Emerged and mature lateral roots with organized cell files. The majority of the GFP-ROP6 and GFP-rop6CA proteins were concentrated on proximal anticlinal cell borders (arrows). In the meristematic zone, the protein was distributed more or less evenly around the cells. Q to S, GFP-rop6DN was observed in pROP6>>GFP-rop6DN seedlings in lateral root founder cells (Q), stage II/II LRI cells (R), and leaf epidermis pavement cells (S). The recruitment of GFP-rop6DN to the plasma membrane is compromised, and it accumulates in the cytoplasm and nuclei in roots (arrows). T, Nonprenylated GFP-rop6CA mutant accumulates in cytoplasm and nuclei (arrows) but, unlike GFP-rop6DN, does not affect cell polarity. Bars = 20 μm.