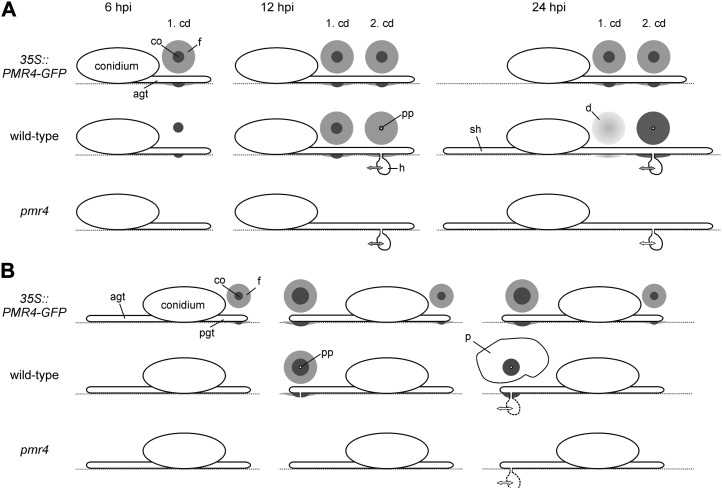
Figure 6.
Schematic overview of callose-based resistance in compatible and incompatible Arabidopsis-powdery mildew interaction. The progress of pathogen-induced callose deposition in 35S::PMR4-GFP, pmr4, and wild-type epidermal leaf cells is shown. Circles represent the shape and size of callose deposits at the indicated time points post inoculation in the compatible interaction of Arabidopsis with the powdery mildew Gc (A) and in the incompatible interaction with the powdery mildew Bgh (B). The grayscale indicates the density of deposited callose. Double-headed arrows suggest possible plant-pathogen interactions responsible for successful pathogen propagation. The coloring of double-headed arrows represents the putative level of interaction: gray, wild-type level (host); white, reduced level (resistant host). agt, Appressorial germ tube; cd, callose deposit; co, core of the callose deposit; d, diffuse callose deposit; f, field of callose; ht, haustorium; p, patch-like callose deposition; pgt, primary germ tube; pp, penetration peg; sh, secondary hyphae.