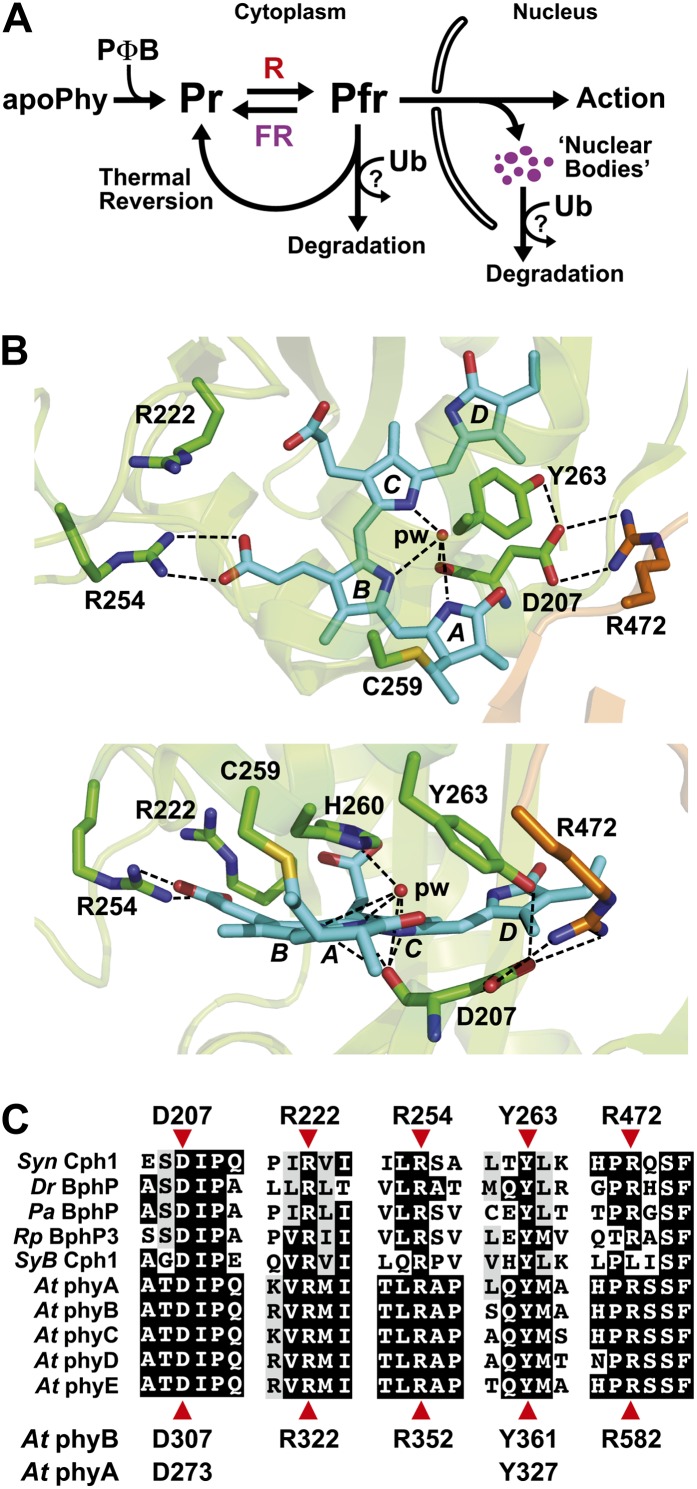
Figure 1.
Scheme of phy action and the three-dimensional relationships of key amino acids within the bilin-binding PSM. A, Scheme depicting the main steps involved in phy assembly, Pr/Pfr photointerconversion, stability, aggregation, and action in higher plants. Photoconversion, thermal reversion, and possibly degradation likely occur in both the cytoplasm and nucleus. B, Top (top) and side (bottom) three-dimensional views of the PSM from Syn-Cph1 (Protein Data Bank code no. 2VEA; Essen et al., 2008) assembled with phycocyanobilin, highlighting the positions of key conserved amino acids surrounding the bilin and the Cys involved in bilin attachment (Cys-259). The residue numbers are those for Syn-Cph1. The GAF domain and PHY hairpin are colored in green and orange, respectively. Phycocyanobilin is in cyan, with the individual pyrrole rings labeled. Sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms are colored yellow, red, and deep blue, respectively. Important contacts are indicated by dashed lines. pw, Pyrrole water. C, Alignment of the GAF domain and PHY hairpin protein sequences among bacterial phys with available structures and with comparable sequences from the phyA to phyE family in Arabidopsis. Residues pertinent to this study are indicated by red arrowheads; their sequence positions are shown either above for Syn-Cph1 or below for Arabidopsis phyA and phyB. At, Arabidopsis; Pa, Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Rp, Rhodopseudomonas palustris.