Fig. 1.
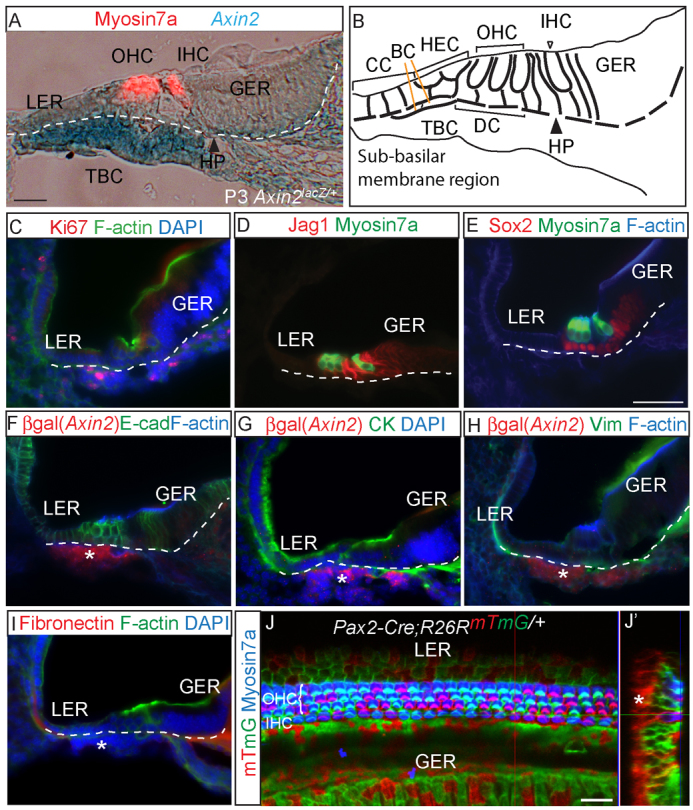
Axin2 expression in tympanic border cells and their lineage origin. (A) Cryosection of X-gal-stained P3 Axin2lacZ/+ cochlea demonstrating intense LacZ (Axin2) expression among tympanic border cells (TBCs) beneath the basilar membrane (dotted line). Myosin 7a marks outer and inner hair cells (OHCs and IHCs). (B) The location of TBCs in the cochlea in relation to the sensory epithelium (SE). (C) TBCs are proliferative and express Ki67. (D,E) Expression of jagged 1 (Jag1) and Sox2 was restricted to SE-supporting cells and absent in TBCs. (F-I) Anti-β-galactosidase antibody was used to detect Axin2-lacZ-positive TBCs (asterisks) in the P1 Axin2lacZ/+ cochlea. Both epithelial (cytokeratin and E-cadherin) and mesenchymal markers [vimentin (Vim) and fibronectin] were absent in TBCs. (J) Whole-mount cochleae from P1 Pax2-Cre;R26RmTmG/+ demonstrating traced mGFP-positive cells in the SE but not in TBCs. (J′) Reconstructed cross-section of z-stack images. Asterisk indicates TBCs. BC, Boettcher cells; CC, Claudius cells; HEC, Hensen’s cells; DC, Deiters’ cells; HP, habenula perforata; LER, lesser epithelial ridge; GER, greater epithelial ridge. Scale bars: 25 μm in A,J,J′; 50 μm in C-I.
