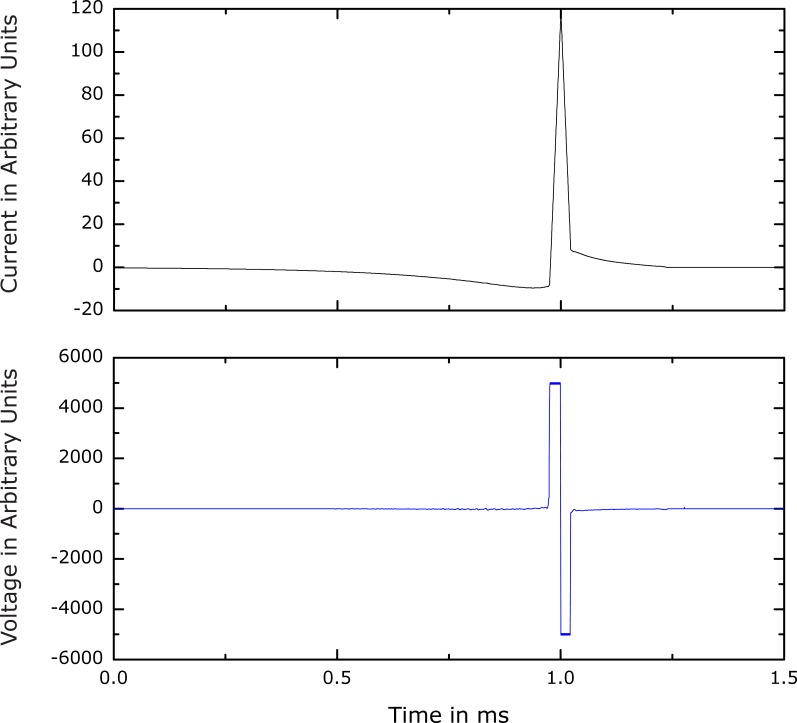
Figure 2. Current and voltage waveform.
These plots correspond to waveform (c) in Figure 1. As defined in Section Objectives and Method Overview, the voltage refers to the inductive component of the coil and is directly proportional to the derivative of the current. Both voltage and current are scaled in arbitrary units. The absolute values of the current and voltage waveforms depend on many additional parameters such as coil design, inductance, distance to target, etc. The rise time of the main phase of the current pulse is 23 µs. The maximum derivative within the first phase is about 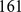 times lower than the slopes of the second phase. Despite the low amplitude, the long duration results in an area under the initial current phase that is higher than the area under the second phase by approximately
times lower than the slopes of the second phase. Despite the low amplitude, the long duration results in an area under the initial current phase that is higher than the area under the second phase by approximately 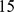 %.
%.