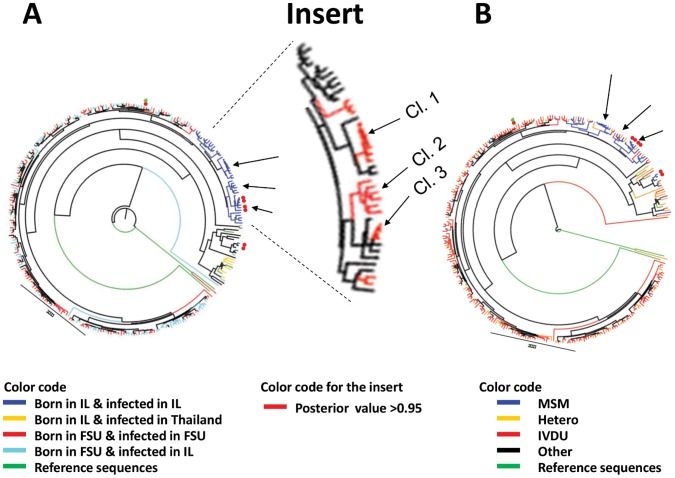
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree of Pr-RT sequences from A/AE-HIV samples.
Neighbor-joint analysis of A/AE protease and RT sequences, combined (918 nucleotides). The first available sequence from 216 drug-naive and 65 drug-treated individuals was used. Trees were colored according to: A. Birth place and infection site: red lines – born and infected in FSU; blue lines – born and infected in Israel; turquoise lines – born in FSU and infected in Israel; yellow lines – born in Israel and infected in Thailand; green lines – reference sequences. B. Transmission groups: red lines – IVDU; blue lines – MSM; turquoise lines – Hetero; green lines – reference sequences. Insert: red lines – posterior probability>0.95 of having a common ancestor. Major drug-resistance mutations in drug naive individuals: Red circles – K103N; Green triangle – M184V; orange rhombus – protease M46I. Reference sequences used in constructing the tree: Subtype-A/AE variants: subtype A – AF193275, subtype CRF01_AE – AF197340 and AF447851.1; subtype CRF03_AB – AF193276; subtype B – K03455, subtype C – AF286233 and AY585268; subtype D – AY322189; subtype F – AJ249238. Cl. – cluster. Clusters having more than 4 members with posterior probability>0.95 of having a common ancestor are marked with arrows.