Abstract
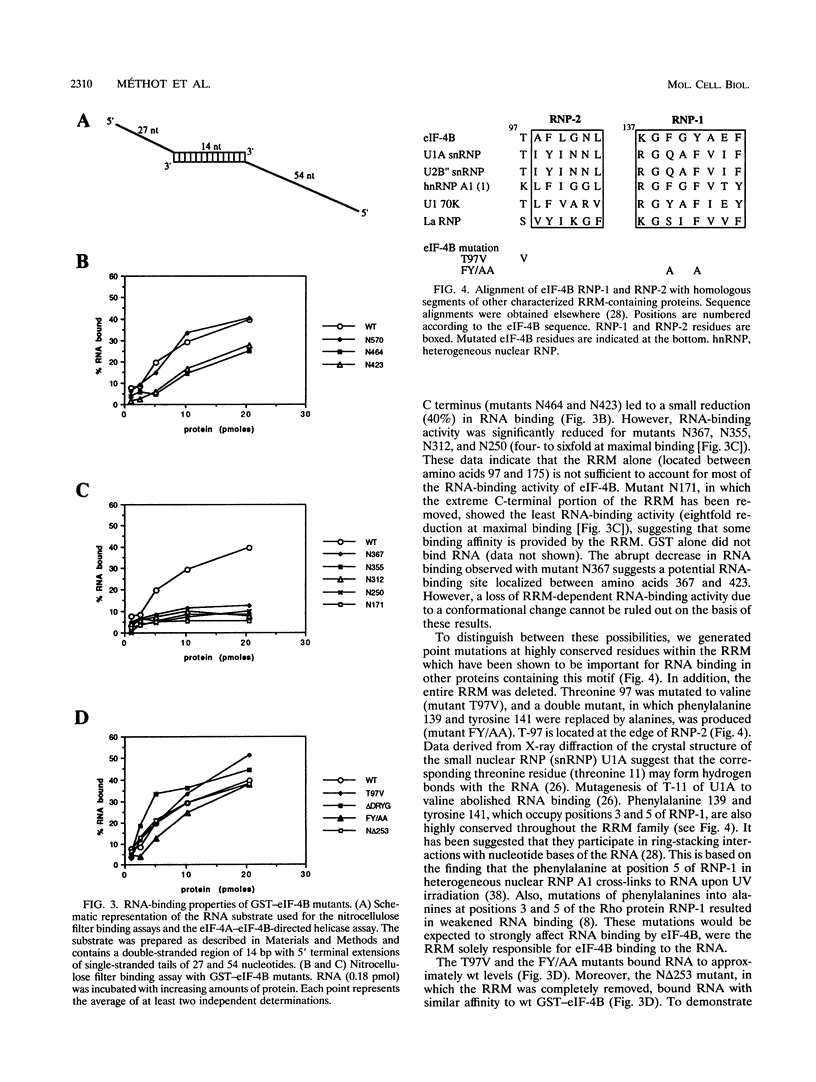
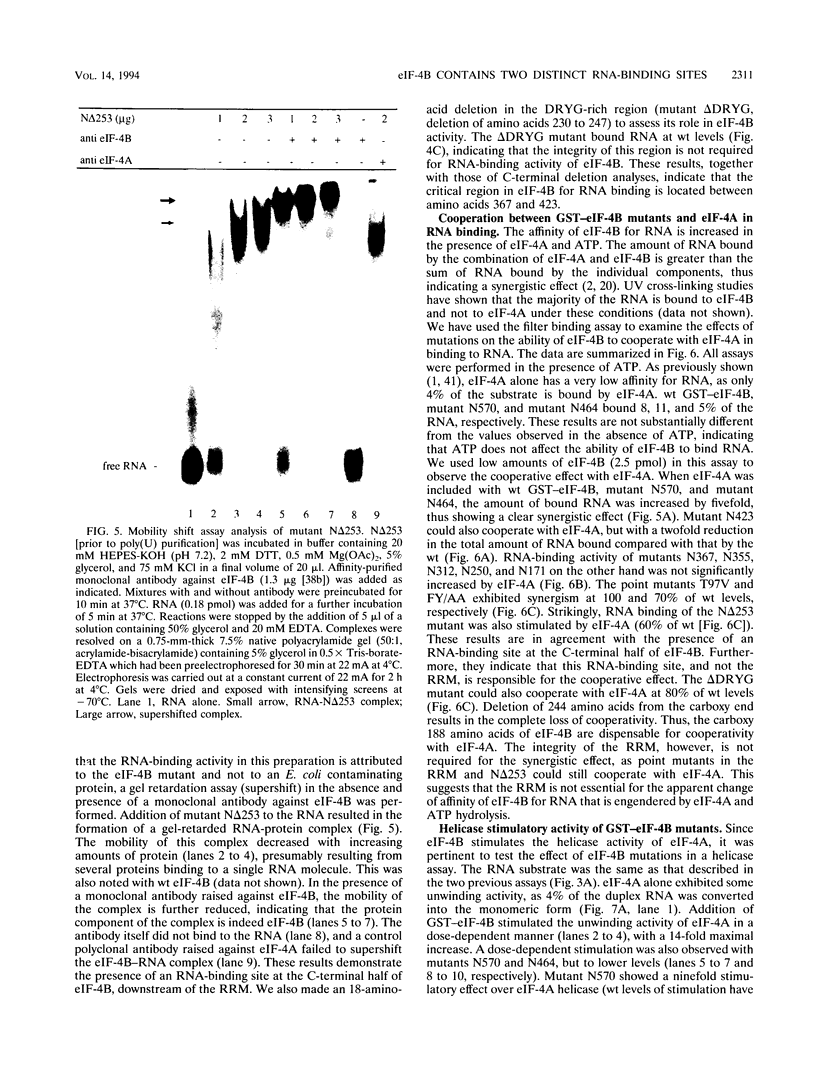
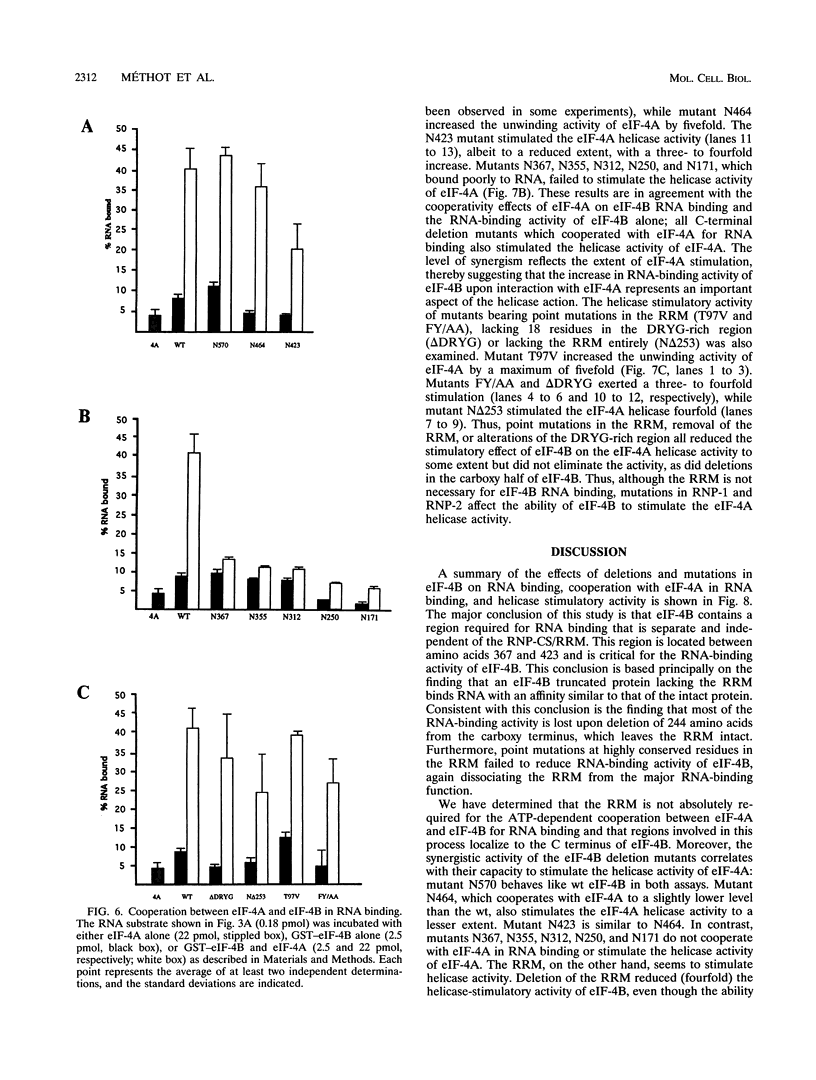
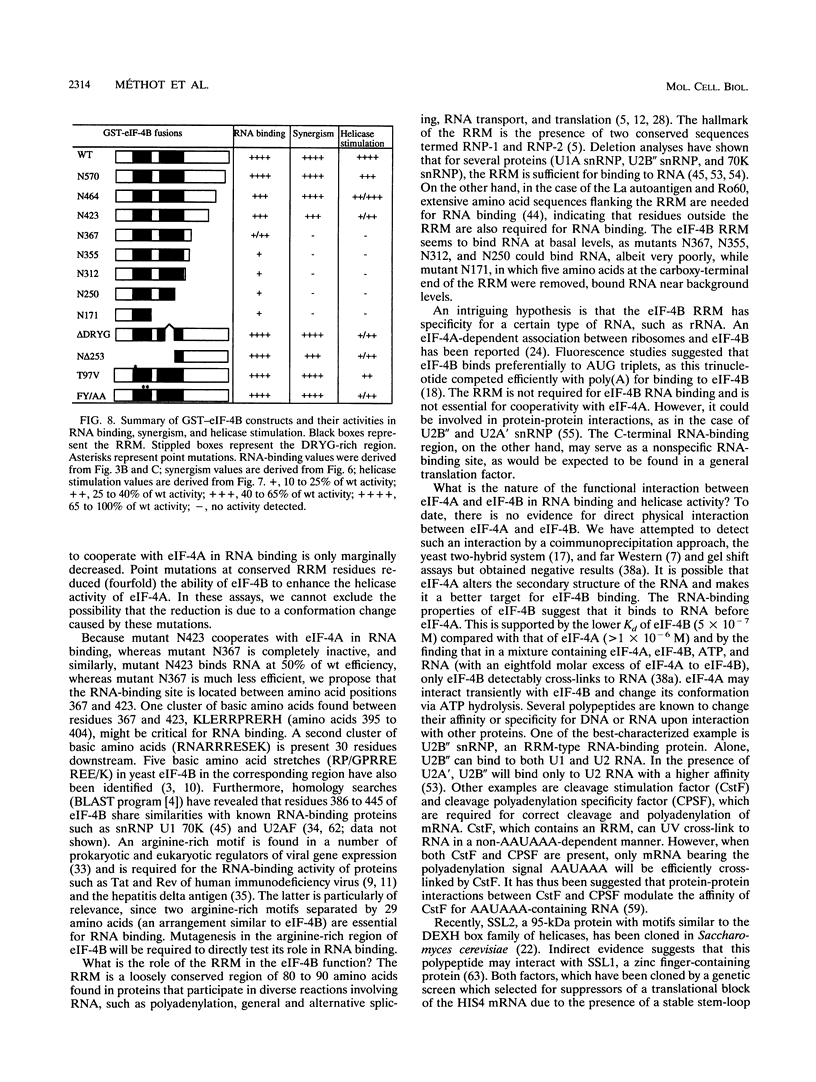
eIF-4B is a eukaryotic translation initiation factor that is required for the binding of ribosomes to mRNAs and the stimulation of the helicase activity of eIF-4A. It is an RNA-binding protein that contains a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence (RNP-CS)/RNA recognition motif (RRM). We examined the effects of deletions and point mutations on the ability of eIF-4B to bind a random RNA, to cooperate with eIF-4A in RNA binding, and to enhance the helicase activity of eIF-4A. We report here that the RNP-CS/RRM alone is not sufficient for eIF-4B binding to RNA and that an RNA-binding region, located between amino acids 367 and 423, is the major contributor to RNA binding. Deletions which remove this region abolish the ability of eIF-4B to cooperate with eIF-4A in RNA binding and the ability to stimulate the helicase activity of eIF-4A. Point mutations in the RNP-CS/RRM had no effect on the ability of eIF-4B to cooperate with eIF-4A in RNA binding but significantly reduced the stimulation of eIF-4A helicase activity. Our results indicate that the carboxy-terminal RNA-binding region of eIF-4B is essential for eIF-4B function and is distinct from the RNP-CS/RRM.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson R. D., Dever T. E., Lawson T. G., Ray B. K., Thach R. E., Merrick W. C. The ATP-dependent interaction of eukaryotic initiation factors with mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3826–3832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson R. D., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C. Biochemical evidence supporting a mechanism for cap-independent and internal initiation of eukaryotic mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6016–6019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann M., Müller P. P., Wittmer B., Ruchti F., Lanker S., Trachsel H. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae homologue of mammalian translation initiation factor 4B contributes to RNA helicase activity. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3997–4003. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06077.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R., Hershey J. W. The mechanism of action of protein synthesis initiation factors from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3078–3087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Rutter W. J. Interaction cloning: identification of a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that interacts with c-Fos. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1014–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.1589769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan C. A., Platt T. Mutations in an RNP1 consensus sequence of Rho protein reduce RNA binding affinity but facilitate helicase turnover. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17296–17305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnan B. J., Biancalana S., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. Analysis of arginine-rich peptides from the HIV Tat protein reveals unusual features of RNA-protein recognition. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):201–210. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppolecchia R., Buser P., Stotz A., Linder P. A new yeast translation initiation factor suppresses a mutation in the eIF-4A RNA helicase. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):4005–4011. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06078.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delling U., Roy S., Sumner-Smith M., Barnett R., Reid L., Rosen C. A., Sonenberg N. The number of positively charged amino acids in the basic domain of Tat is critical for trans-activation and complex formation with TAR RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6234–6238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Matunis M. J., Piñol-Roma S., Burd C. G. hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:289–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Hershey J. W. Heat shock-induced translational alterations in HeLa cells. Initiation factor modifications and the inhibition of translation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11882–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Hershey J. W. Regulation of initiation factors during translational repression caused by serum depletion. Covalent modification. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5493–5497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Hümbelin M., Darveau A., Lee K. A., Milburn S., Hershey J. W., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Involvement of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A in the cap recognition process. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Hansen J., Ehrenfeld E., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Milburn S., Hershey J. W. Demonstration in vitro that eucaryotic initiation factor 3 is active but that a cap-binding protein complex is inactive in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):832–837. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.832-837.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss D. J., Woodley C. L., Wahba A. J. A fluorescence study of the binding of eucaryotic initiation factors to messenger RNA and messenger RNA analogues. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1551–1556. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Satler C. A., Merrick W. C. RNA-stimulated ATPase activity of eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8648–8654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Leis J. P., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. Characterization of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A, a protein involved in ATP-dependent binding of globin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5246–5252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. New initiation factor activity required for globin mRNA translation. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5804–5810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyas K. D., Donahue T. F. SSL2, a suppressor of a stem-loop mutation in the HIS4 leader encodes the yeast homolog of human ERCC-3. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):1031–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90621-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R. The RNP motif protein family. New Biol. 1992 May;4(5):421–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. L., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C. Further biochemical characterization of rabbit reticulocyte eIF-4B. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Mar;301(2):311–319. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagus R., Anderson W. F., Safer B. The regulation of initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;25:127–185. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60484-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen T. H., Oubridge C., Teo C. H., Pritchard C., Nagai K. Identification of molecular contacts between the U1 A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein and U1 RNA. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3447–3456. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04909.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D., Query C. C. Nuclear RNA-binding proteins. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;41:179–202. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koromilas A. E., Lazaris-Karatzas A., Sonenberg N. mRNAs containing extensive secondary structure in their 5' non-coding region translate efficiently in cells overexpressing initiation factor eIF-4E. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4153–4158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T. G., Lee K. A., Maimone M. M., Abramson R. D., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Dissociation of double-stranded polynucleotide helical structures by eukaryotic initiation factors, as revealed by a novel assay. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4729–4734. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazaris-Karatzas A., Montine K. S., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a eukaryotic initiation factor subunit that binds to mRNA 5' cap. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):544–547. doi: 10.1038/345544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. G., Zamore P. D., Green M. R., Hurwitz J. RNA annealing activity is intrinsically associated with U2AF. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13472–13478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Z., Lin J. H., Chao M., McKnight K., Lai M. M. RNA-binding activity of hepatitis delta antigen involves two arginine-rich motifs and is required for hepatitis delta virus RNA replication. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2221–2227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2221-2227.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. RNA recognition: a family matter? Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):837–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90265-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C. Mechanism and regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jun;56(2):291–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.2.291-315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill B. M., Stone K. L., Cobianchi F., Wilson S. H., Williams K. R. Phenylalanines that are conserved among several RNA-binding proteins form part of a nucleic acid-binding pocket in the A1 heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3307–3313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn S. C., Hershey J. W., Davies M. V., Kelleher K., Kaufman R. J. Cloning and expression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4B cDNA: sequence determination identifies a common RNA recognition motif. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2783–2790. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07466.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley S. J., Traugh J. A. Differential stimulation of phosphorylation of initiation factors eIF-4F, eIF-4B, eIF-3, and ribosomal protein S6 by insulin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10611–10616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pause A., Méthot N., Sonenberg N. The HRIGRXXR region of the DEAD box RNA helicase eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A is required for RNA binding and ATP hydrolysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6789–6798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pause A., Sonenberg N. Mutational analysis of a DEAD box RNA helicase: the mammalian translation initiation factor eIF-4A. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2643–2654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05330.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Insertion mutagenesis to increase secondary structure within the 5' noncoding region of a eukaryotic mRNA reduces translational efficiency. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., Slobbe R. L., van Venrooij W. J. Analysis of protein--RNA interactions within Ro ribonucleoprotein complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5173–5180. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Lawson T. G., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Recycling of messenger RNA cap-binding proteins mediated by eukaryotic initiation factor 4B. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11466–11470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Lawson T. G., Kramer J. C., Cladaras M. H., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. ATP-dependent unwinding of messenger RNA structure by eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7651–7658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Edery I., Meerovitch K., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Sonenberg N. Bidirectional RNA helicase activity of eucaryotic translation initiation factors 4A and 4F. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1134–1144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Knippers R., Stahl H. RNA unwinding activity of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):955–963. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90334-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., Dathan N. A., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. Major determinants of the specificity of interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1A and U2B'' and their cognate RNAs. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):502–506. doi: 10.1038/345502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., van Venrooij W. J., Dathan N. A., Hamm J., Mattaj I. W. Identification of the RNA binding segment of human U1 A protein and definition of its binding site on U1 snRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4163–4170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Dathan N. A., Boelens W., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. The U2B'' RNP motif as a site of protein-protein interaction. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3675–3681. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Cap-binding proteins of eukaryotic messenger RNA: functions in initiation and control of translation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:173–207. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Morgan M. A., Merrick W. C., Shatkin A. J. A polypeptide in eukaryotic initiation factors that crosslinks specifically to the 5'-terminal cap in mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., MacDonald C. C., Shenk T., Manley J. L. The human 64-kDa polyadenylylation factor contains a ribonucleoprotein-type RNA binding domain and unusual auxiliary motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1403–1407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Erni B., Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. II. The assembly of the initiation complex with purified initiation factors. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):755–767. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):505–510. doi: 10.1126/science.2200121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valcárcel J., Singh R., Zamore P. D., Green M. R. The protein Sex-lethal antagonizes the splicing factor U2AF to regulate alternative splicing of transformer pre-mRNA. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):171–175. doi: 10.1038/362171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon H., Miller S. P., Pabich E. K., Donahue T. F. SSL1, a suppressor of a HIS4 5'-UTR stem-loop mutation, is essential for translation initiation and affects UV resistance in yeast. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2463–2477. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]