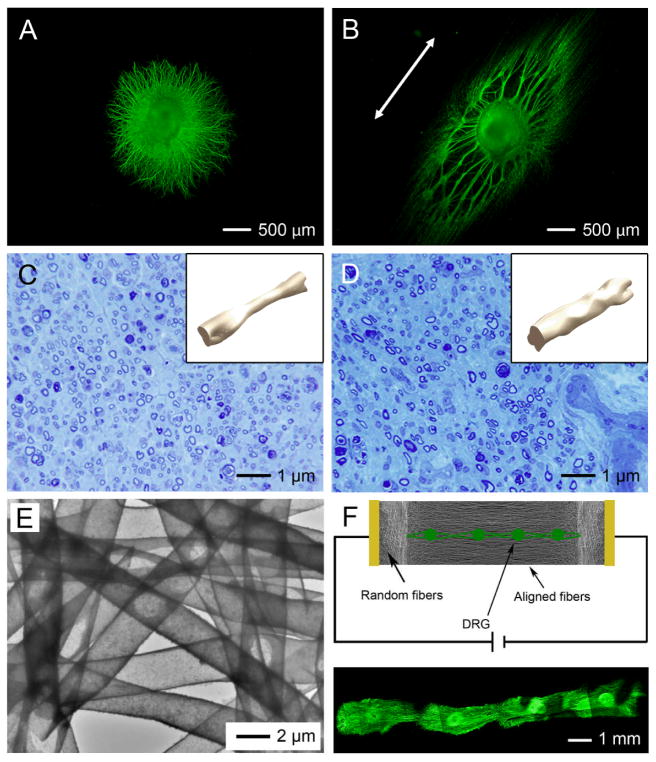
Figure 5.
Scaffolds of electrospun nanofibers for neural tissue engineering. A, B) Chicken dorsal root ganglia (DRG) cultured on scaffolds consisting of (A) random and (B) aligned nanofibers. Fiber alignment (as marked by the double-headed arrow) induced significantly longer extension of neurites from the DRG. C, D) Optical micrographs showing Toluidine Blue staining of a cross section at the midpoint of the nerve regenerated from distal parts through the guidance of (C) a silicone tube and (D) a conduit made of poly(3-caprolactone) nanofibers. The insets show isometric views of the regenerated nerves inside the silicone tube and the nanofiber-based conduit, respectively. E) Hollow nanofibers of polypyrrole (PPy) fabricated by dissolving the original PCL fibers after PPy coating. F) Electrical stimulation on multiple DRG cultured on a scaffold of aligned hollow PPy nanofibers led to the extension and potential connection of neurites from different DRG. Reproduced with permission: (A, B) from ref. [81], copyright2010 American Chemical Society; (C, D) from Ref. [85], copyright 2010 RSC Publishing; and (E, F) from Ref. [95], copyright 2009 Wiley-VCH.