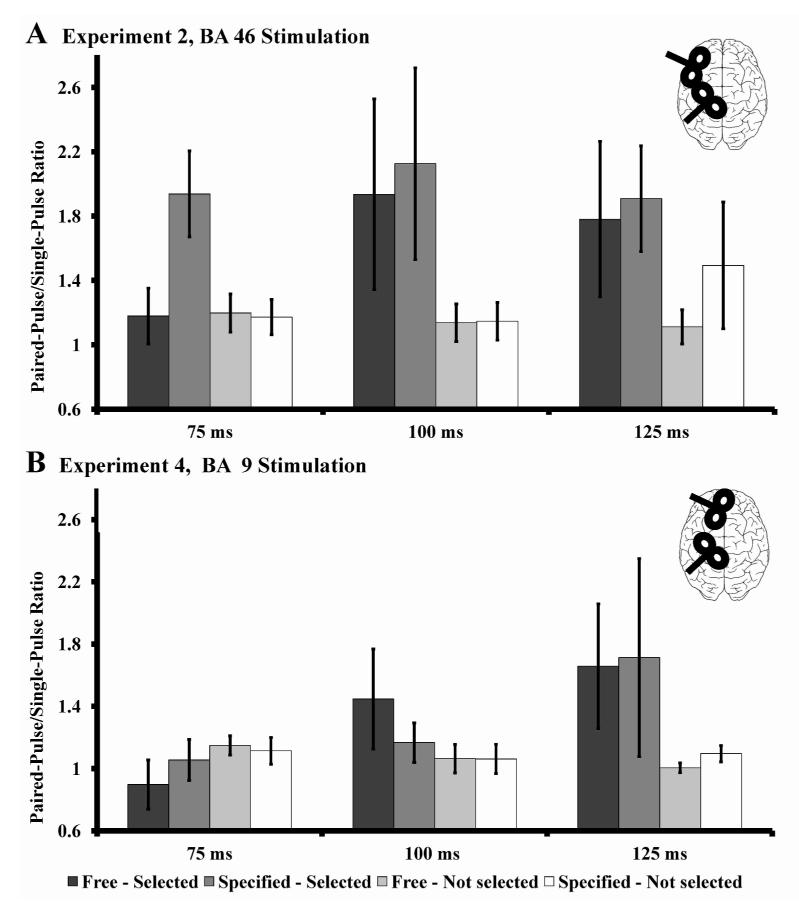
Figure 3.
Timing of the specific functional connectivity with regard to muscle-involvement (data recorded from the right FDI, experiment 2 and 4). A) BA 46 stimulation: The difference between free and externally specified conditions disappeared (compare to figure 2, experiment 1) when a task specific muscle was investigated (significant main effect of “selection”). Different relay stations of BA46, like premotor cortices, might influence the BA46-M1 connectivity when task-specific, selected muscles are investigated. B) BA 46 stimulation: Analyses did not reveal an effect of BA 9 stimulation and the initially described effect (A) disappeared. The visual difference at a SOA of 125 ms is due to an outlier and not statistically significant. The data of 75 ms and 100 ms shows clearly that BA 46 stimulation has an impact on selected movements and the stimulation of BA 9 is not able to replicate this finding. Error bars are expressed as standard error of the mean.