Figure 2.
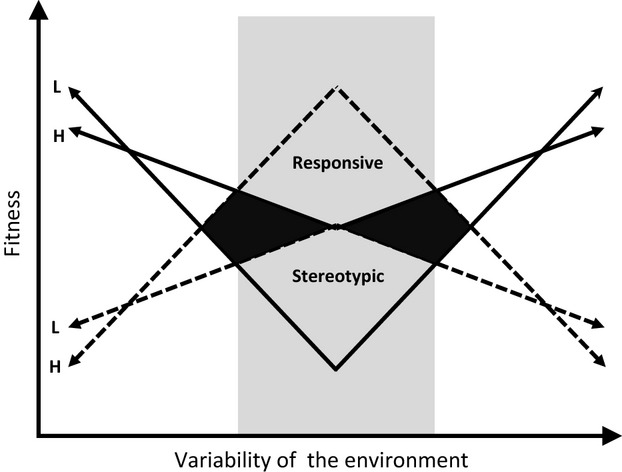
Behavioral type-dependent fitness benefits of information usage within and between behavioral types in environments with different environmental variability. In grey area the benefits of cognition exceeds its costs. Therefore, responsive behavioral types (dashed line) with high (H) and low (L) cognitive abilities dominate in these kinds of environments, compared with stereotypic behavioral types (solid lines) that instead dominate in invariable or highly variable environments (i.e. outside grey area). Variation in cognitive abilities within and between behavioral types leads to environment-dependent coexistence of different behavioral types (black area). In the grey area the high plasticity and flexibility in behavior potentially restricts the consistency in behaviors in time and across contexts and therefore, may limit the abundance or affect the expression of animal personalities.
