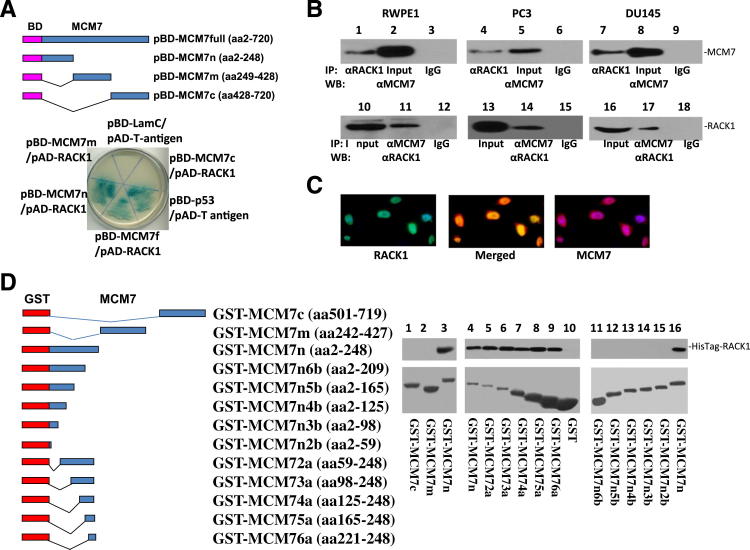
Figure 1.
N-terminus of MCM7 binds with RACK1. A: Constructs of full length (pBD-MCM7full), N-terminus (pBD-MCM7n), mid segment (pBD-MCM7m), and C-terminus (pBD-MCM7c) of MCM7 with bait domain (BD) in yeast two-hybrid analysis. Co-transformants of pBD-MCM7full or pBD-MCM7n, or pBD-MCM7m or pBD-MCM7c with pAD-RACK1 on SD agar plate with high stringent nutrient selection (SD-leu-Trp-His-Ade) are shown. Co-transfection of pBD-p53 and pAD-T-antigen is the positive control, whereas co-transfection of pBD-LamC and pAD-T-antigen is the negative control. B: Co-immunoprecipitation of MCM7 (lanes 1 to 9) or RACK1 (lanes 10 to 18) using antibodies specific for RACK1 or MCM7 to immunoprecipitate from RWPE1 (left panels), PC3 (middle panels), and DU145 cells (right panels). The immunoprecipitates were blotted with the indicated antibodies. C: Immunofluorescence staining of RWPE-1 cells with antibody against RACK1 bound by fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibody for mouse and antibody specifically against MCM7 recognized by TRITC conjugated secondary antibody for rabbit. D: Mapping binding motif of RACK1 on MCM7. Left: Constructs of series of MCM7 deletion mutants with GST expression vectors. Right: Binding assays on GST or GST-MCM7 deletion mutants with RACK1 from PC3 cells (lanes 1 to 3) or HisTag-RACK1 (lanes 4 to 16). The bound RACK1 was blotted with anti-RACK1 antibodies. Top blots: Immunoblots with antibodies specific for RACK1. Bottom blots: Coomassie staining of proteins.