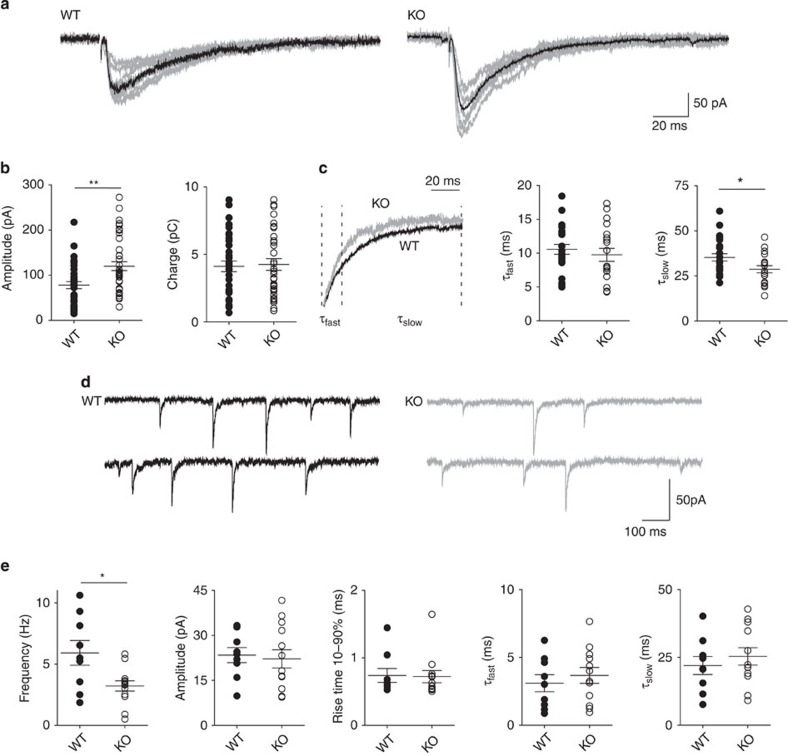
Figure 1. Syn II deletion modifies the dynamics of the evoked GABA response.
(a) Representative traces of eIPSCs from WT and KO dentate gyrus granule neurons (the average trace is shown in black). (b) Mean (±s.e.m.) amplitude and charge of eIPSCs (closed and open circles represent single experiments for WT and KO neurons, respectively). (c) The decay of the WT eIPSC (left panel; black trace) was normalized to the peak amplitude of the KO eIPSC (grey trace). A two-exponential model was used to fit the fast and slow components of the decay (τfast and τslow) and their average values (±s.e.m.) are shown in the middle and right panels, respectively. *P<0.05, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. n=23 and n=30 neurons for WT (10 mice) and KO (15 mice), respectively. Analysis of eIPSC kinetics showed that the latency (2.06±0.19 and 1.78±0.28 ms, for WT and KO neurons, respectively, P=0.45) and rise time (2.74±0.34 and 2.85±0.32 ms, for WT and KO neurons, respectively, P=0.81) were similar between genotypes (data not shown). (d) Representative traces of mIPSCs recorded in dentate gyrus granule neurons from WT (black) and KO (grey) mice. (e) Aligned dot plots of frequency, amplitude and kinetic parameters (rise time; τfast; τslow ) of mIPSCs in neurons from WT (closed symbols) and KO (open symbols) mice. Each dot represents one experiment. *P<0.05, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. n=9 and n=13 neurons from WT (4 mice) and KO (6 mice), respectively.