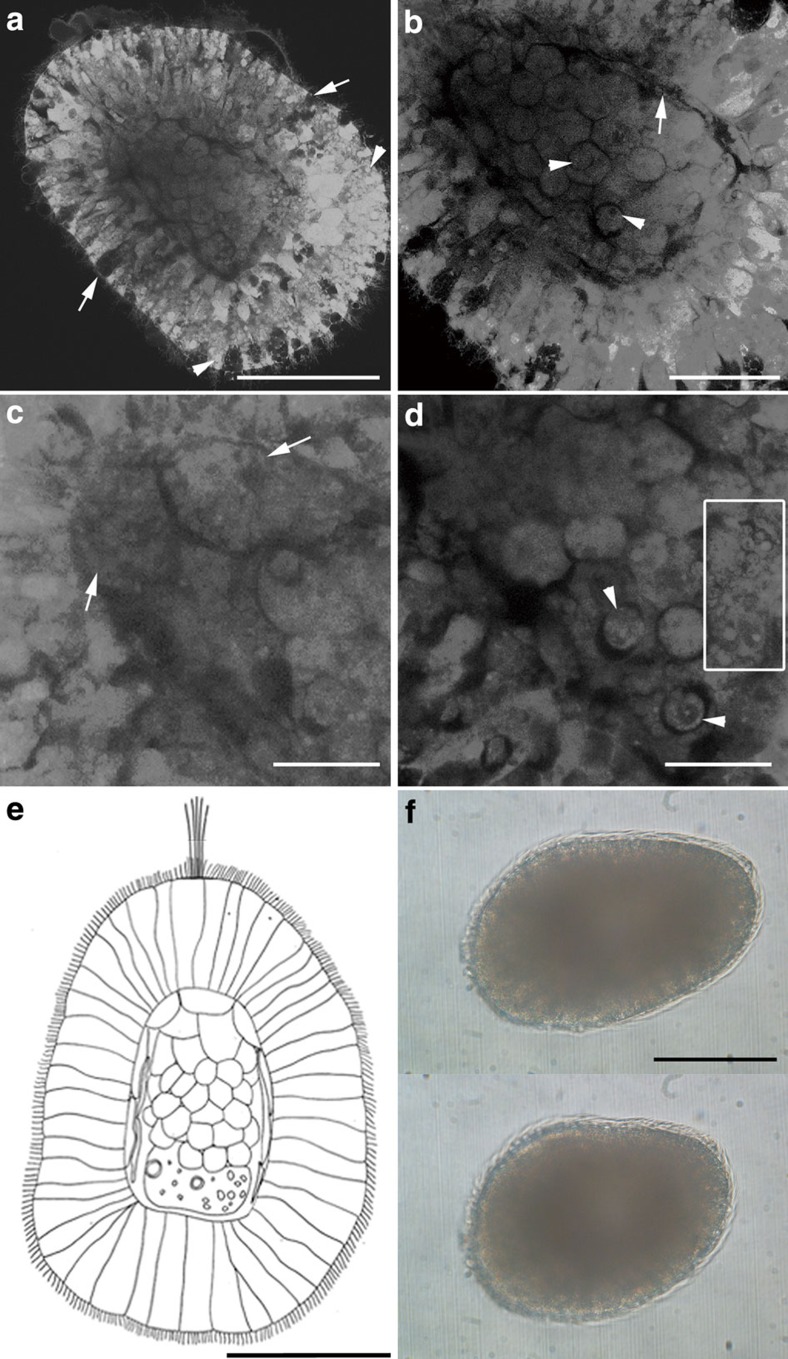
Figure 2. Free-swimming stages of Xenoturbella bocki.
(a–d) Confocal microscopy, 4 days after hatching with anterior at upper left. (a) Epithelial ectoderm (developing to epidermis) with glandular cells (arrows) and vesicles (arrowheads) surrounding the internal cell mass (developing to gastrodermis). (b) Thin dark layer of developing subepidermal muscle cells (arrow) surrounds the gastrodermal cell mass, composed of rounded cells. Arrowheads point to the nuclei of the rounded cells. (c) Large cells in the anterior part of the internal cavity (arrows). (d) Small cells (arrowheads) and extracellular vesicles (inside square) in the posterior part of the internal cavity. (e) Diagram of a 4-day hatchling of Xenoturbella bocki, based on the specimen in a. Anterior to top. (f) Free-swimming specimen 5 days after hatching before (upper panel) and after (lower panel) contracting the body. Anterior end at left. Scale bars, 100 μm (a,e,f); 50 μm (b); 25 μm (c,d).