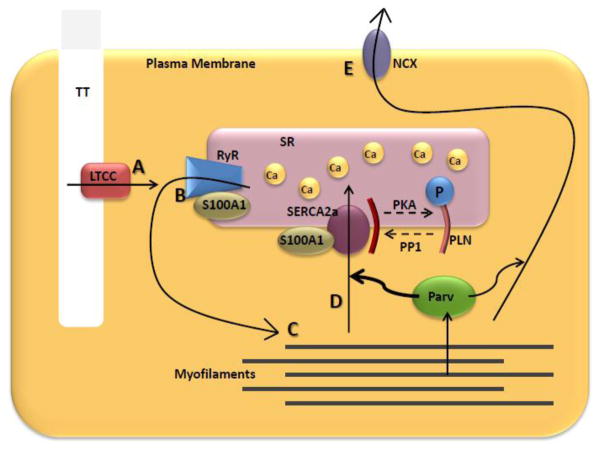
Figure 1.
Calcium Cycling in the Cardiac Myocyte. Arrows represent Ca2+ flux during one contractile cycle. A) Action potential allows Ca2+ entry through the LTCC, which B) triggers a much larger Ca2+ release from the SR through the RyR. C) Ca2+ binds to myofilament proteins, leading to force production. D) Ca2+ is then taken back up into the SR via SERCA2a, or E) pumped out of the cell via NCX. S100A1 and PLN act as modulators of Ca2+ transport protein function. Parv buffers Ca2+ away from myofilaments after force production.