Figure 1.
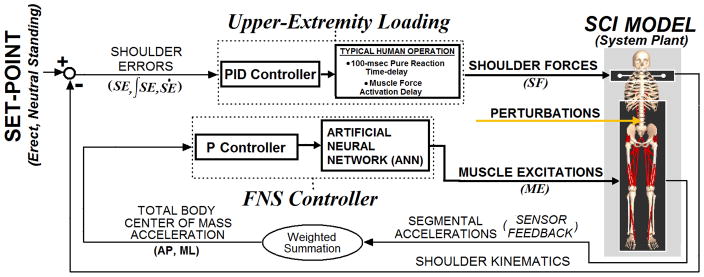
Overall model system. Two parallel controllers act to maintain the 3-D model of bipedal SCI stance at setpoint position against postural perturbations: (1) A FNS controller modulates trunk, lower-extremity muscle excitations according to COM acceleration feedback in the AP and ML directions driving an ANN. The ANN is trained to output muscle excitation changes that counter measured effects induced by disturbances and net recovery responses upon the COM. (2) An upper-extremity (UE) controller, representing user volitional loading, produces three-dimensional point forces at the shoulders according to position errors relative to the shoulder set-point posture. COM acceleration and shoulder positional errors are expressed in globally-fixed 3-D Cartesian coordinates. The gains for UE control are determined according to Ziegler-Nichols tuning rules. FNS controller gains are optimized using global-search algorithm to minimize UE controller output (“loading”) against perturbations.
