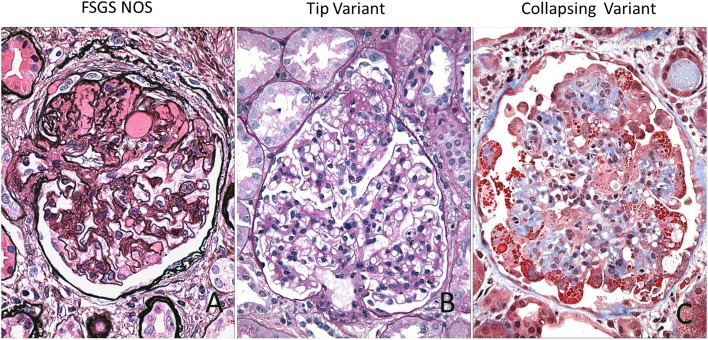
Figure 1.
Major histologic variants are illustrated. (A) Not otherwise specified (NOS) is the common generic form of FSGS, and it exhibits segmental solidification of the tuft by extracellular matrix (in this case, involving approximately half of the tuft with hyalinosis, loss of overlying podocytes, and adhesion to Bowman’s capsule [Jones methenamine silver, ×600]). (B) The tip variant displays a segmental lesion located at the tubular pole with adhesion to the tubular neck and confluence of podocytes and parietal epithelial cells (Periodic acid Schiff, ×400). (C) The collapsing variant has implosive wrinkling and retraction of glomerular basement membranes with hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the overlying glomerular epithelial cells, which contain abundant fuchsinophilic protein resorption droplets (Masson trichrome, ×400).