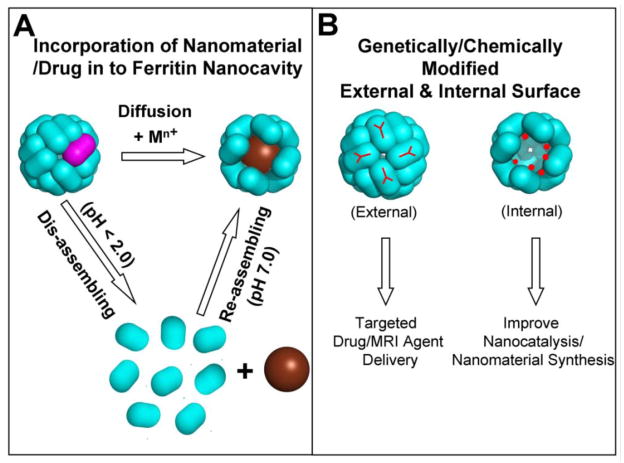
Figure 3. Synthesis and incorporation of nanomaterials/nanoparticles inside the multi-subunit ferritin nano cavity for catalysis and targeted drug delivery.
A. The smaller chemicals, preferably positive charged metal complexes easily diffuse in to the ferritin nanocavity through the 3-fold ion channels by incubation with the intact ferritin cage and nanoparticle synthesis takes place inside the cavity. Bigger nanoparticles (< 8 nm) encapsulated by disassembling/reassembling of multi-subunit ferritin nanocage. B. Both external and internal ferritin cage surfaces modified either by genetically/or chemically to use ferritin nanocage containing nanomaterial for the targeted delivery and to improve catalysis/synthesis. Purple-ferritin polypeptide subunits.