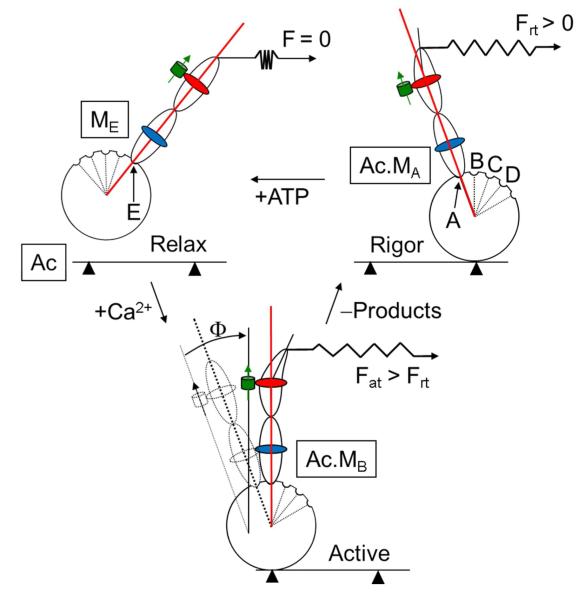
Figure 3.
Simplified cross-bridge cycle in contraction detailing myosin’s discrete sub-states (A-E) and their correspondence to lever-arm orientation. The rigor cross-bridge binds actin (Ac) in the A-state (MA), exerts force Frt, and maintains the PAGFP (green cylinder with arrow) tagged HCRLC (red) in the A-state orientation. ELC is shown in blue. ATP addition relaxes the fiber by binding to myosin and detaching actin. The relaxed cross-bridge assumes the E-state (ME) with the lever-arm re-primed for a new power stroke. Ca2+ addition activates the fiber producing force Fat. In isometric contraction single lever-arms assume one of their intermediates (A-E) depicted here as MB which is a high force producing intermediate having a characteristic orientation indicated by Φ.