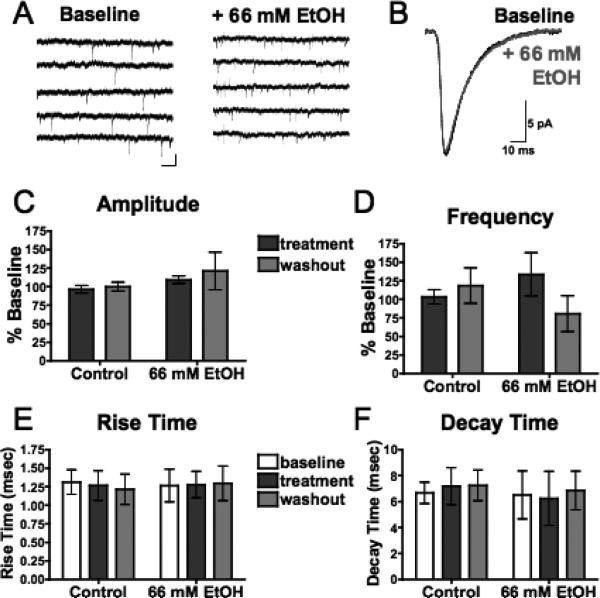
Fig. 3.
Acute ethanol has no effect on spontaneous AMPAR-mediated EPSCs (sEPSCs) in mPFC pyramidal neurons. (A) Representative traces containing sEPSCs from PFC pyramidal neurons in the presence of picrotoxin (100 μM) and DL-APV (100 μM) before (left) and after (right) acute exposure to ethanol (66 mM). Scale bar: 25 pA, 5 ms. (B) Averaged sEPSCs before (black) and after (gray) acute exposure to ethanol (66 mM). (C,D) Average sEPSC amplitude (C) and frequency (D) normalized to baseline during (dark gray) and 15 to 20 minutes following (light gray) sham solution exchange (n=7) or acute exposure to 66 mM ethanol (n=5). (E,F) sEPSC rise time (E) and decay time (F) before (white), during (dark gray), and 15 to 20 minutes following (light gray) sham solution exchange or acute exposure to 66 mM ethanol. Values are expressed as averages ± SEM.