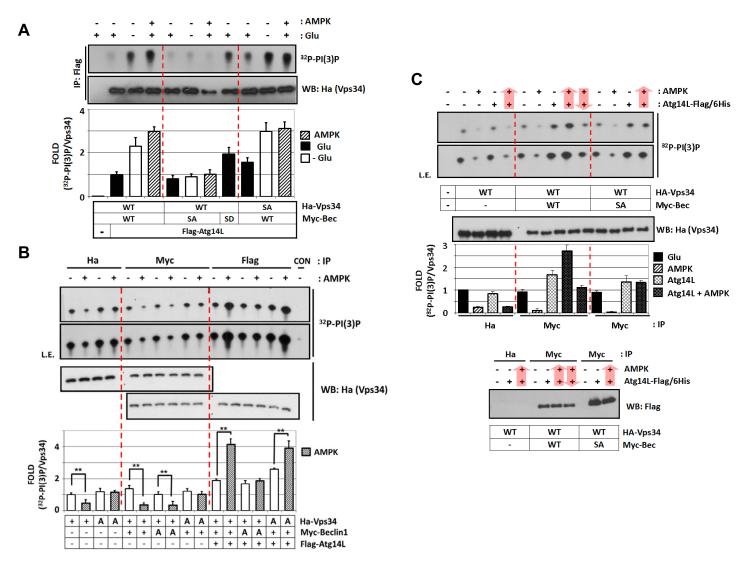
Fig.4.
Phosphorylation of Beclin1 and Vps34 are required for the regulation of Vps34 complexes by glucose starvation or AMPK.
(A) Beclin1 phosphorylation, but not Vps34 phosphorylation, is required for Atg14L-associated Vps34 complex activation in response to glucose starvation. Wild-type (WT), phosphorylation defective (SA), -mimetic (SD) Ha-Vps34, Myc-Beclin1 and Flag-Atg14L were co-transfected with AMPK into HEK293 cells as indicated. The cells were glucose-starved for 3 hrs (n=3).
(B) Phosphorylation of Vps34 and Beclin1 is required for Vps34 regulation by AMPK. Vps34 complexes were immuno-purified by HA (Vps34), Myc (Vps34-Beclin1), or Flag (Vps34-Beclin1-Atg14L) and then incubated with AMPK for 15 min in vitro before Vps34 lipid assay (n=3). +, wild-type; A, a phosphorylation-defective mutant.
(C) Atg14L determines whether Vps34-Beclin1 complex is activated or inhibited by AMPK. Vps34 complex was immuno-purified by either HA (Vps34) or Myc (Vps34-Beclin1) from the transfected HEK293 cells, to which purified Atg14L was added, and then treated with AMPK as indicated by arrow for order of the treatment. Atg14L protein level in the complexes was determined by western blot (bottom panel) (n=2).
Data are represented as mean ± S.D.