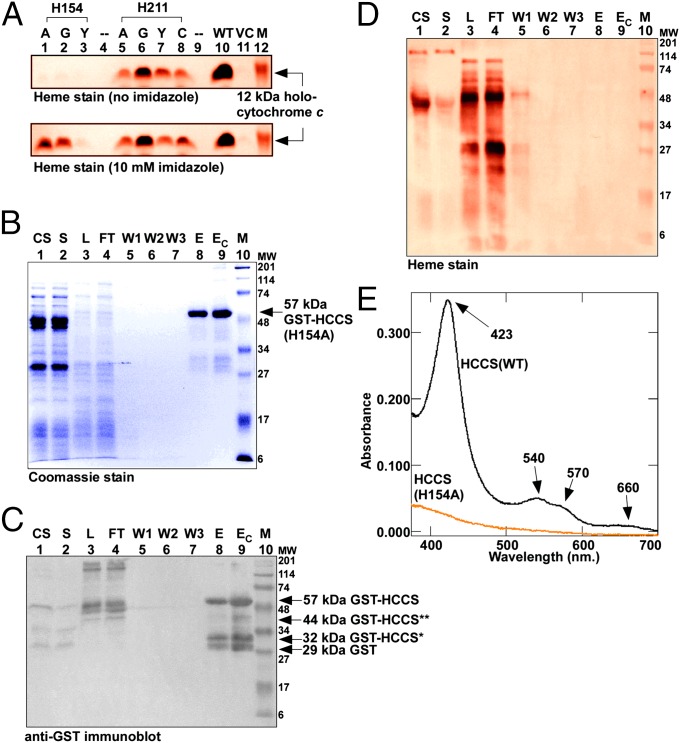
Fig. 2.
HCCS His154 is a heme ligand. (A) Heme staining of cell extracts (B-PER) showing covalent 12-kDa holocytochrome c assembled by WT and site-directed mutants of HCCS in the E. coli cytoplasm in the absence (Upper) or presence (Lower) of 10 mM imidazole added to culture. His154 was changed to alanine (lane 1), glycine (lane 2), or tyrosine (lane 3); His211 was changed to alanine (lane 5), glycine (lane 6), tyrosine (lane 7), or cysteine (lane 8). M, molecular weight standards; VC, vector control. (B) Coomassie blue staining showing purified 57-kDa full-length GST-tagged HCCS(H154A). (C) Anti-GST immunoblot showing 57-kDa full-length GST-tagged HCCS(H154A), 44- and 32-kDa degradation products, and 29-kDa GST. (D) Heme staining of purified 57-kDa full-length GST-HCCS. For B–D abbreviations are as follows: CS, crude sonicate; E, elution; EC, concentrated elution; FT, flow through; L, load (DDM-solubilized membranes); M, molecular weight standards; S, soluble fraction; W1, wash 1; W2, wash 2; W3, wash3. For A and D, prestained molecular weight standards were overlaid in red onto the heme stains. (E) UV-Vis absorption spectra of purified GST-HCCS(H154A) (orange line) shown with the spectrum of purified GST-HCCS(WT) (black line).