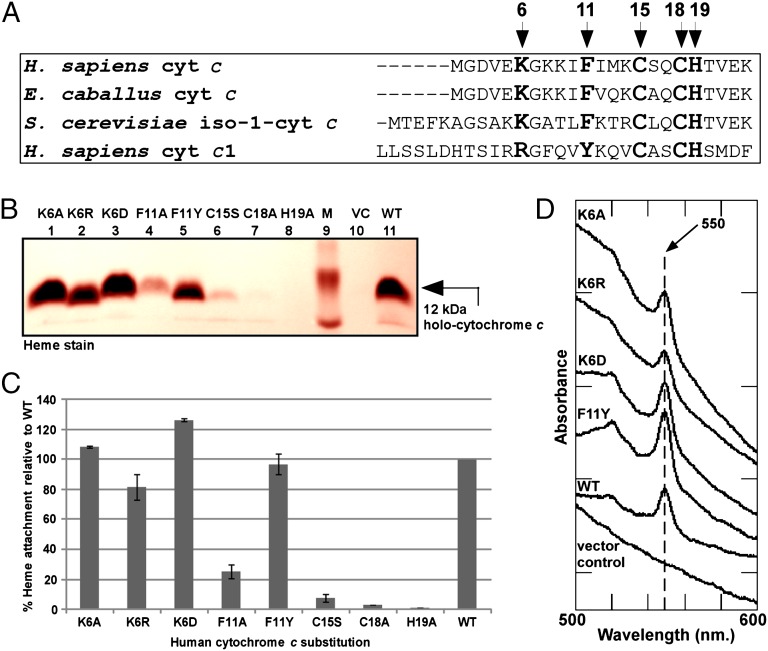
Fig. 3.
Maturation determinants in human cytochrome c. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the region encompassing the heme-attachment site (CXXCH) for the indicated cytochromes c and c1. The amino acids mutated in this work are shown in bold and are indicated by arrows; numbering begins at the N-terminal methionine in H. sapiens cytochrome c. (B) Representative heme stainingof B-PER extracts showing synthesis of 12-kDa WT holocytochrome c and the indicated cytochrome c variants by the human HCCS. M, molecular weight standards; VC, vector control. One hundred micrograms of total protein was loaded in each lane. Prestained molecular weight standards were overlaid in red onto the heme stain. (C) Quantification of the results of heme staining of B-PER extracts from three independent experiments. Percent heme attachment for each variant is relative to synthesis of WT cytochrome c, which has been set at 100%. Error bars denote SD. (D) UV-Vis absorption spectra of B-PER extracts from cells expressing HCCS along with the indicated cytochrome c variant.