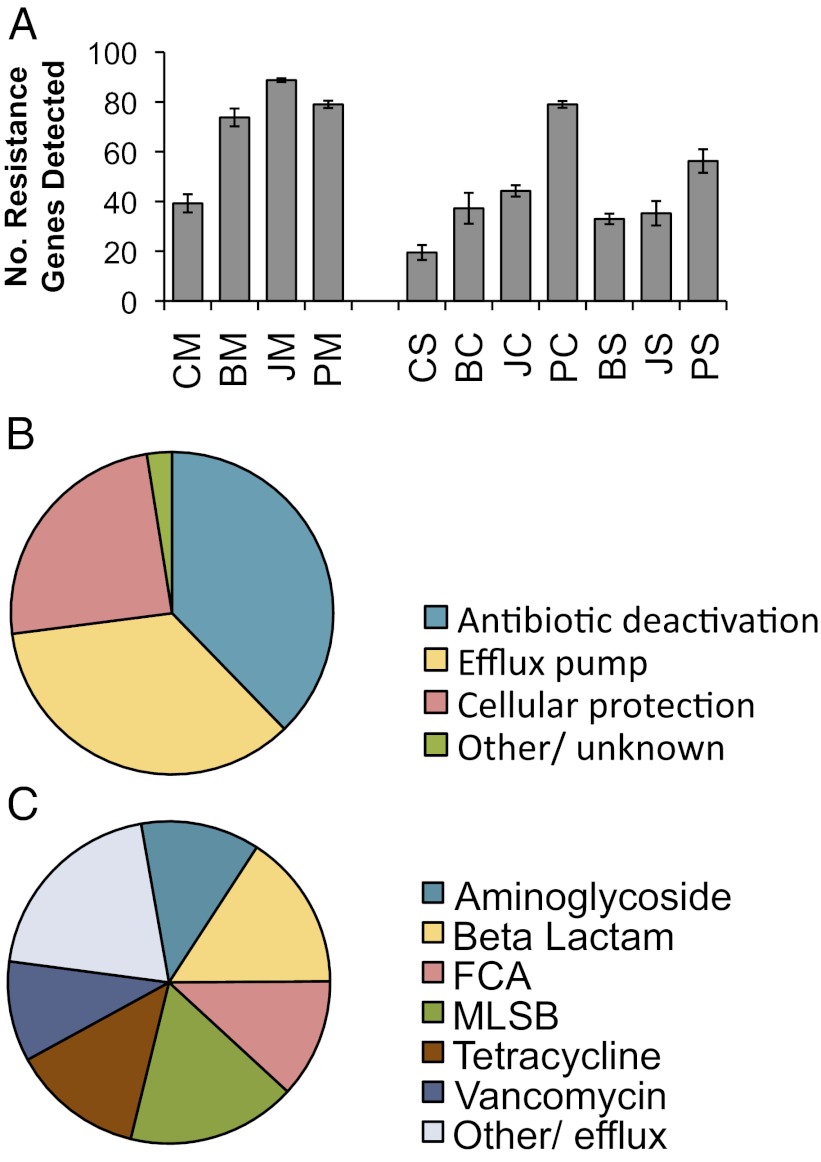
Fig. 1.
Antibiotic resistance gene detection statistics. Sample names are abbreviated with two letters representing location and sample type: first C, B, J, and P (control, Beijing, Jiaxing, and Putian, respectively) and second M, C, and S [manure, compost, and soil (with compost amendment), respectively]. Because many resistance genes were targeted with multiple primers, if multiple primer sets detected the same gene, this was only counted as detection of a single unique resistance gene. (A) Average number of unique resistance genes detected in each sample. Error bars represent SEM of four field replicates. The resistance genes detected in all samples were classified based on (B) the mechanism of resistance, and (C) the antibiotic to which they confer resistance. FCA, fluoroquinolone, quinolone, florfenicol, chloramphenicol, and amphenicol resistance genes; MLSB, Macrolide-Lincosamide-Streptogramin B resistance.