Fig. 3.
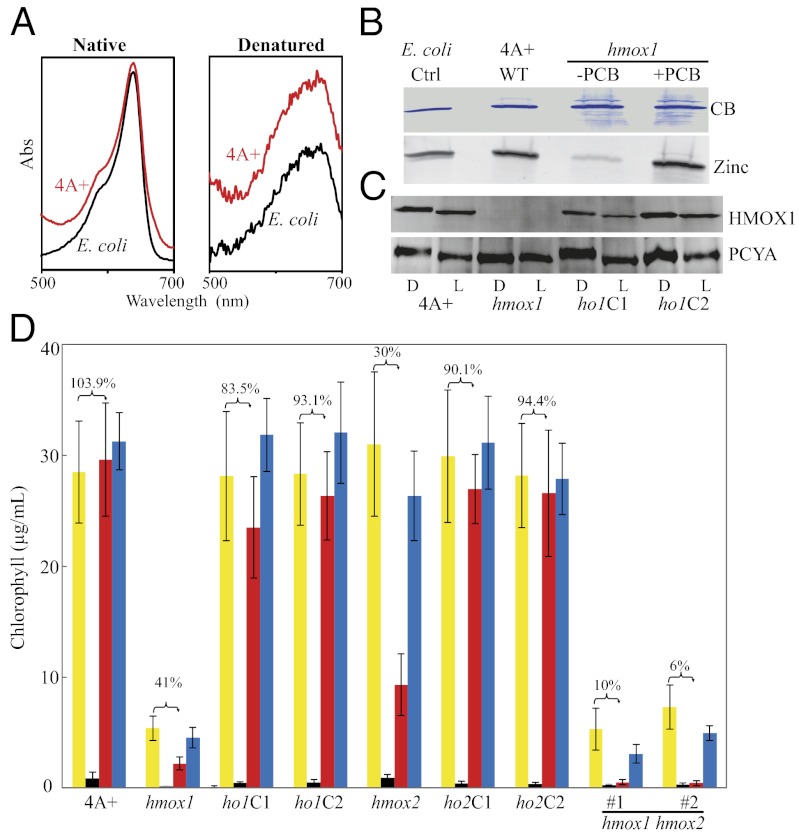
Chloroplast HMOX1 is responsible for synthesis of phycocyanobilin (PCB), and both heme oxygenases participate in heme iron assimilation in vivo. (A) Absorption spectra of native and denatured PCB-adducts of chloroplast-targeted cyanobacteriochrome NpF2164g5 purified from C. reinhardtii wild-type strain 4A+ or from PCB-producing E. coli. (B) NpF2164g5 purified from transgenic 4A+, hmox1, or E. coli cultures analyzed by Coomassie Blue (CB) staining (Upper) or by zinc-dependent fluorescence (Lower) for the presence of covalently bound PCB. Purified NpF2164g5 protein from hmox1 cells was still capable of binding PCB in vitro. (C) Immunoblot analysis of HMOX1 and PCYA in 4A+, hmox1, and two hmox1 complementing lines (ho1C1 and ho1C2) grown in suspension culture heterotrophically in darkness (D) or photoautotrophically under continuous light (L) at a fluence rate of 100 μmol photons⋅m−2⋅s−1. (D) Growth of C. reinhardtii with exogenous heme as iron source as measured by stationary-phase chlorophyll levels. All strains were grown in complete TAP medium (yellow columns), iron-free medium (black), or iron-free medium supplemented with either 10 µM hemin (red) or 20 µM Fe3+ (blue). The percent chlorophyll content of hemin-supplemented cultures relative to those grown on complete medium is shown for each genotype. Bars indicate the SD of three to four replicates.