Fig. 2.
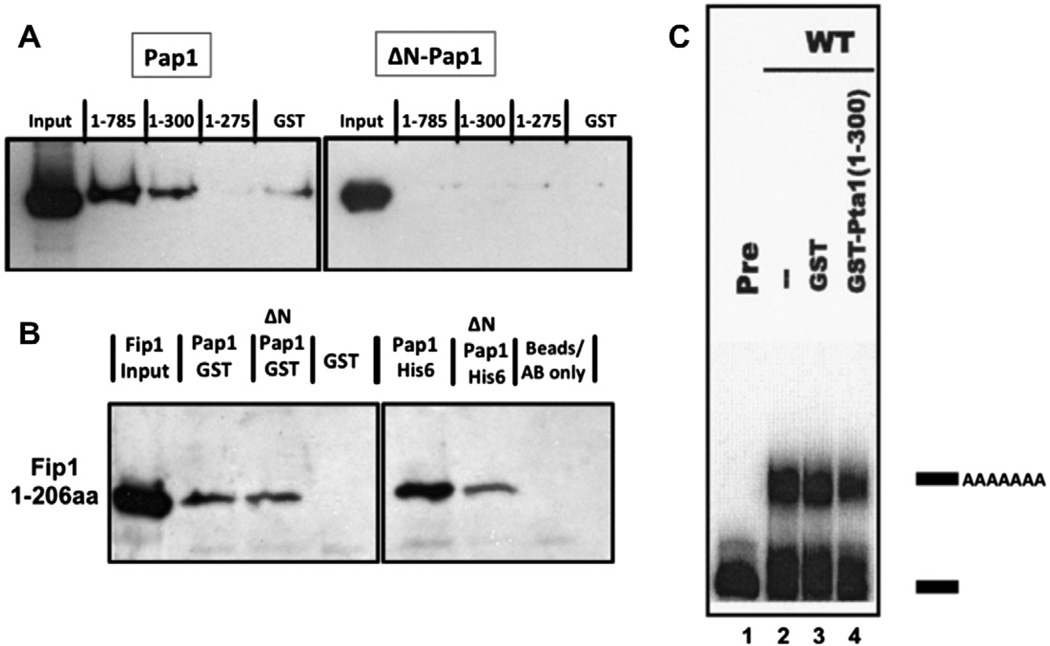
Pta1 interacts directly with the Pap1 N-terminus. (A) Western blot showing the amount of Pap1-His6 or ΔN-Pap1-His6 pulled down with full-length GST-Pta1 or the indicated Pta1 fragments. (B) Western blot showing that full-length Pap1 and ΔNPap1 interact with amino acids 1–206 of Fip1 [11]. Left panel: Fip1 pull-downs with the Pap1-GST, ΔNPap1-GST, or GST proteins used in Figs. 2A and 4. Right panel: co-immunoprecipitations of Fip1 using Pap1-His6 or ΔNPap1-His6 immobilized on protein A beads by Pap1 antibody, or using beads and antibody without Pap1. (C) Addition of the 1–300 amino-acid fragment of Pta1 inhibits poly(A) addition performed with yeast extract and radioactive GAL7 RNA substrate ending at the poly(A) site. Lane 1, unreacted precursor (Pre); lane 2, extract alone; lane 3, extract plus GST; lane 4, extract plus GST-Pta1 (1–300). Positions of precursor and polyadenylated RNAs are indicated on the right.