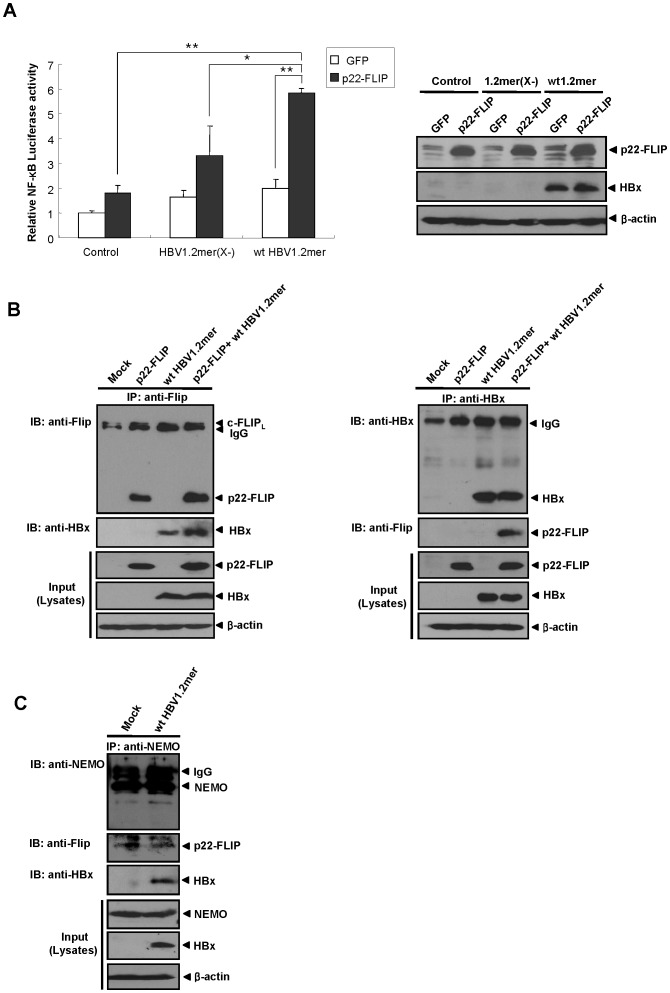
Figure 6. p22-FLIP synergistically enhances HBx-induced NF-κB signaling in the context of replication-competent HBV through interaction with HBx.
(A) p22-FLIP synergistically enhances HBx-mediated NF-κB signaling in the context of HBV full genome. Relative NF-κB activity (left panel) was measured at 48 hours post-transfection of pNF-κB-Luc(0.25μg) and the indicated plasmids (0.4μg) in Huh7 cells. Total amounts of DNA were adjusted by pCMV vector. Results were obtained by at least four independent experiments (*, P = 0.011; **, P<0.001). Expression levels of p22-FLIP and HBV genome-driven HBx were determined by Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies (right panel). (B) p22-FLIP physically interacts with HBV genome-driven HBx in liver cells. At 72 hours post-transfection of wt HBV1.2mer (2μg) and p22-FLIP (2μg) plasmids, Huh7 cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flip (left panel) or anti-HBx (right panel) antibodies, respectively. Total amounts of transfected DNA were adjusted by pcDNA3.1 vector. Western blot analysis was carried out using the indicated antibodies. Cell lysates were used as a positive control. (C) Potential formation of ternary complex among endogenous p22-FLIP, NEMO, and genome-driven HBx in Huh7 cells. Approximately 7.8×106 Huh7 cells were transfected with wt HBV1.2mer plasmids and cultured for 72 hours. Thereafter, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-NEMO antibody and blotted by anti-NEMO, anti-Flip, and anti-HBx antibodies.