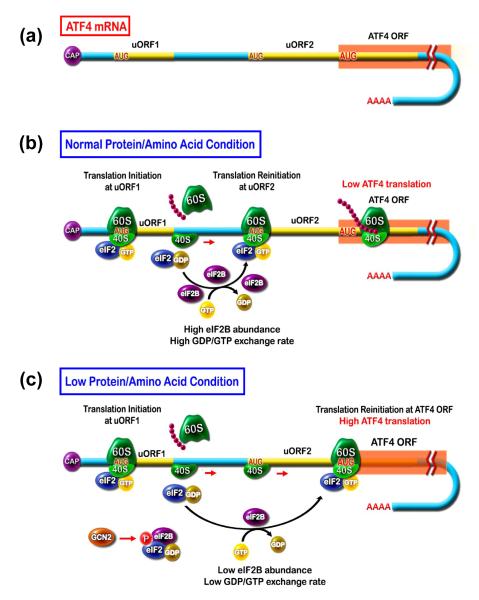
Figure 2.
Synthesis of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) is increased in response to cell stress. (a) The mRNA for ATF4 contains two short upstream open reading frames (uORF). (b) In normal protein/amino acid conditions, ribosomal scanning leads to translation of uORF1 and re-initiation at uORF2, which is out-of-frame and overlaps with the ATF4 coding sequence. Thus, little or no ATF4 is synthesized. (c) During low protein/amino acid conditions, general control non-derepressible 2 (GCN2) phosphorylates eIF2α, which in turn depletes the available GDP-GTP exchange factor, eukaryotic initiation factor 2B (eIF2B), by non-functional binding. Consequently, there is a reduction in active eIF2-GTP and a slower rate of re-initiation after uORF1 translation. As a result, ribosome assembly occurs after the AUG in uORF2 and coincident with translation of the ORF encoding ATF4. In this way, increased ATF4 protein production occurs only during periods of cellular stress.