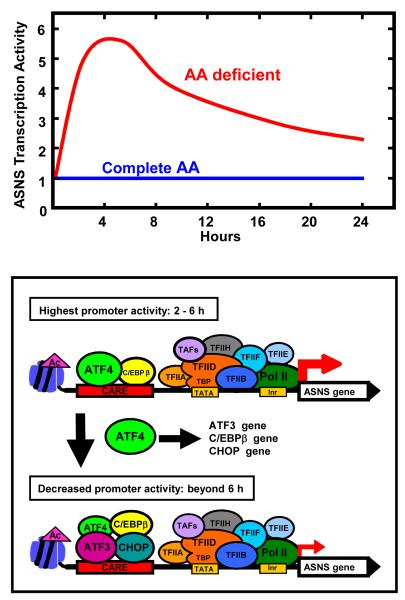
Figure 4.
(a) Model for activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) self-limiting regulation of the asparagine synthetase (ASNS) gene. (b) During the initial 2-6 h of amino acid limitation, enhanced translational control of ATF4 protein production results in increased binding of ATF4 to the AARE. A low level of CCAAT-enhancer binding protein β (C/EBPβ) is constitutively bound. In parallel with ATF4 binding, histone acetylation occurs and the general transcription machinery is recruited to the promoter. Beyond 6 h, ATF4 action has caused increased expression of C/EBPβ and ATF3 proteins, and their binding to the C/EBP-ATF response element (CARE) increases coincident with a decline in the transcription activity of the ASNS gene. The C/EBP homology protein (CHOP) gene represents a variation on this general theme given that it also requires phospho-ATF2 and p300/CBP associated factor (PCAF). Ac, acetylated (histone); CHOP, C/EBP homology protein Inr, initiator sequence; Pol II, RNA polymerase II; TAF, TBP associated factors; TBP, TATA binding protein; TATA, TBP binding sequence; TFIIA/B/D/E/F/H, RNA Pol II associated general transcription factors.